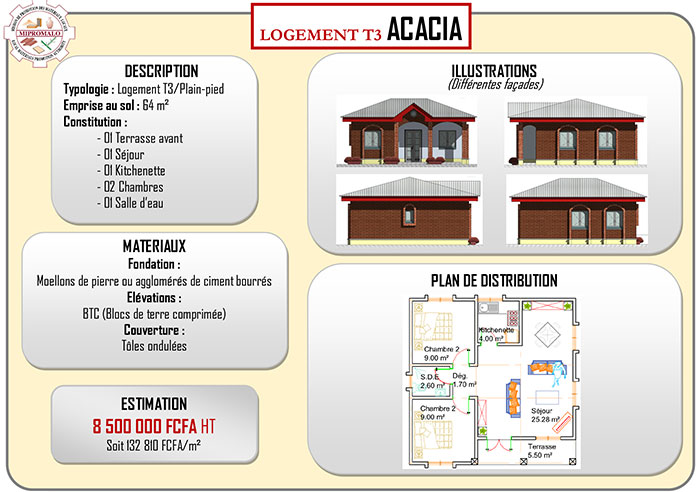
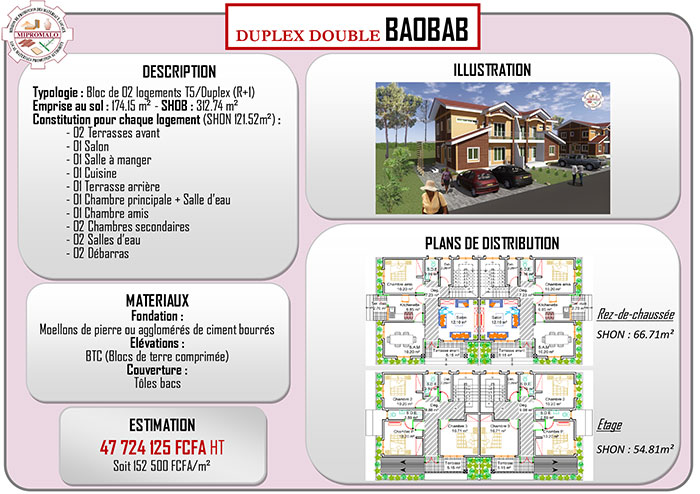
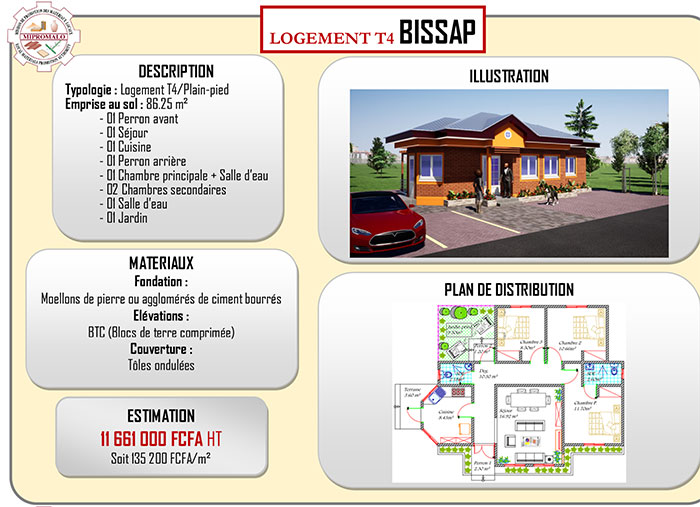
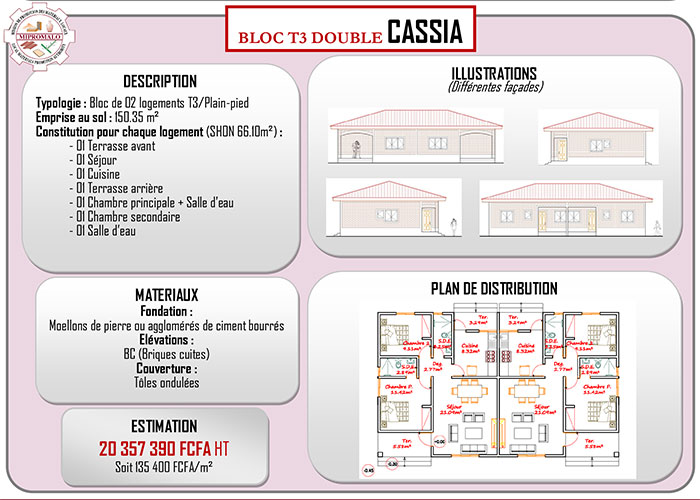
Recherche & Innovation (4)
Download the complete document
|
Sciences des matériaux |
|
[1] J. G. D. Nemaleu et al., « Low-temperature high-strength lightweight refractory composites: Pore structures and insulating properties », Ceramics International, vol. 49, no 14, p. 23510‑23521, 2023. ABSTRAT Functional refractory remains critical due to its intrinsic properties such as: saving space, lightweight and excellent thermal stability to achieve the trade-off between insulating and overall performances. The present study deals with the production of low carbon footprint and lightweight refractory matrices, with controllable pores structures, thermally stable and having low thermal conductivities. The lightweight refractory products were obtained through the direct foaming of geopolymer pastes and sintered from 900 to 1200 °C. The mechanism of pores formation, pores structures and the effect of both sintering temperature and foaming agent ratio on the thermal insulation, physical and microstructural characteristics were evaluated. The results showed that the produced matrices could be described as low thermal conductors, with thermal conductivity values between 0.49 and 0.18 W/mK. The 3D internal pore structures under laser microscopy observations confirms the mechanism of pore enlargement when high concentration of the foaming agent was added. Furthermore, the decomposition of kyanite particles within the matrices, at high temperature, favoured the extend reduction in porosity and the limitation of the liquid phase, by ensuring the formation of macro-porosities sized between 360 μm and 2 mm. The formation of the refractory crystalline phases namely: cordierite, mullite, enstatite, leucite, as well as, kalsilite, acting as filler, ensure thermal stability of the matrices. The produced materials provide an energy-saving, lightweight ceramic foams with high-strength and low thermal conductivities, potential candidates for refractory applications.(Nemaleu et al., 2023) |
|
AUTEUR: Djobo, J. N. Y., & Tome, S. (2024). TITRE : Insights into alkali and acid-activated volcanic ash-based materials : A review. REFERENCE: Cement and Concrete Composites, 105660. ABSTRACT This review provides a comprehensive study of the fundamentals of the alkaline and acid activation of volcanic ashes (VA), for mainstreaming their use as a conventional feedstock for developing geopolymers and their applications. The low reactivity in an alkaline environment is driven by the low content of the amorphous phase and the low solubility of iron, calcium and magnesium at pH > 12. Nevertheless, techniques such as mechanochemical activation has significantly improved the reactivity and the properties of the resulting products. In the acid phosphate medium, the high solubility of iron, calcium and magnesium ensures good reactivity and a high reaction rate at room temperature. As a result, the engineering properties of acid-phosphate-activated volcanic ash are superior to those of alkali-activated volcanic ash. The resulting materials have great potential for use as binders in concrete design, for the stabilization of compressed earth bricks and for the rapid repair of deteriorated concrete structures. However, significant research is required to fully understand their durability performances, life cycle and techno-economic viability for large-scale utilisation. Further, the limited availability of phosphate resources makes acid activation not a viable route to activate volcanic ash for building purposes. The acid-activated volcanic ash has potential in waste management applications such as nuclear waste or heavy metal encapsulation. Finally, volcanic ash emerges as a promising raw material for developing sustainable building materials through alkali and acid activation. This holds as its exploitation is non-disruptive, and processing requires less energy compared to calcined clay or fly ash.(Djobo & Tome, 2024) |
|
AUTEURS: Nkwaju, R. Y., Nouping, J. N. F., Bachirou, S., Abo, T. M., Deutou, J. G. N., & Djobo, J. N. Y. (2023). TITRE: Effective Stabilization of Cadmium and Copper in Iron-Rich Laterite-Based Geopolymers and Influence on Physical Properties. REFERENCE: Materials, 16(24), 7605. ABSTRACT This study aimed to investigate the efficiency of a geopolymer binder of the type of Na-poly(ferro–silico–aluminate) as a matrix for the stabilization of heavy metals along with their effect on the development of structural performances. The artificial contamination of soil with ions was carried out and used to prepare an alkali-activated iron-rich lateritic soil binder. Further, various microstructural analyses were carried out to explain the stabilization mechanism. The stabilization efficiency was assessed by leaching tests in de-ionized water and hydrochloric acid (0.1 M, HCl). Then, the physical properties were determined to evaluate the impact of heavy metals on the structural performance of the binder. Results demonstrated that the prepared geopolymer binder has the lowest stabilization capacity in an acidic medium (low pH) than in water with high pH. However, the stabilization of Cu ions was effective at 99%, while the Cd ion is barely retained in the matrix. Firstly, the mechanism consists of chemical bonds through ion exchange with sodium of the Na-poly(ferro–silico–aluminate) network. Secondly, through physical interaction with the pore network of the matrix, the heavy metals induced structural deterioration in the geopolymer matrix with a decrease in the compressive strength and bulk density and an increase of both apparent porosity and water absorption.(Nkwaju et al., 2023) |
|
AUTEUR: Djobo, J. N. Y., Hirsch, T., & Stephan, D. (2023). TITRE: Early age properties and water resistance of calcium hydroxide modified volcanic ash‐based phosphate geopolymer binders. REFERENCE: International Journal of Ceramic Engineering & Science, 5(6), e10188. https://doi.org/10.1002/ces2.10188 ABSTRACT This work aims to improve the early age characteristics and water resistance of volcanic ash-based phosphate geopolymer materials by modifying the chemistry of the binder with calcium hydroxide (CH). Phosphate geopolymer binders with Ca/P molar ratios ranging from 0.49 to 0.80 were prepared. Then the early and late age physical properties were then determined. The hardened binder was characterized by various analytical techniques involving XRD, TGA-DSC, and SEM-EDS. The results showed that the use of CH decreases the initial setting time from several hours to less than 5 min. At the same time, the 1 d compressive strength was increased from 0 to 15 MPa with the increase in the Ca/P molar ratio. Moreover, the slow dissolution rate of volcanic ash was responsible for the low strength at an early age but beneficial to improving the geopolymerisation with time. This favored the high strength of the control phosphate geopolymer, which reached 52.5 MPa at 56d and was higher than those with CH (28.5–45.2 MPa). However, the control phosphate geopolymer had poor water resistance, with strength retention ranging from 21%–57% compared to 76%–90% for phosphate geopolymer with CH. This is because of the leaching of the reactive phase underwater that inhibits further reaction progress. In addition, the modification of the binder chemistry with CH leads to the formation of new calcium phosphate phases that also contribute to enhancing water resistance.(Djobo et al., 2023) |
|
AUTEUR: Kieufack, G., Fagel, N., Tchamba, A. B., Bomeni, I. Y., Ngapgue, F., El Ouahabi, M., & Wouatong, A. S. L. (2023). TITRE: Mineralogical and physico-chemical characterization of alluvial clays from Bamendou-Balessing (West Cameroon) : Suitability for ceramics. REFERENCE: Construction and Building Materials, 407, 133396. ABSTRACT The alluvial clays of Bamendou-Balessing (West Cameroon) are characterized to evaluate their potential for ceramic products. Four representative samples collected in the study area were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared (FTIR), differential thermal analysis (DTA) coupled with thermogravimetry analysis (TG), X-ray fluorescence (XRF) and physical analyses (particle size distribution and consistency limits). Firing properties of the specimens making from alluvial clays were determined. The alluvial clays are composed of clay minerals (45–64 wt%) dominated by kaolinite (92–98 wt%) with variable contents of illite (1–7 wt%) and vermiculite (0–2 wt%). The non-clay mineral phases are quartz (19–38 wt%) associated with variable proportions of K-feldspar (1–17 wt%) gibbsite (2–5 wt%) and goethite (1–12 wt%). The thermal behavior of the clayey samples shows dehydration of gibbsite and goethite at 281–288 °C and dehydroxylation of kaolinite at 521–524 °C. SiO2 (34.5–47.4 wt%), Al2O3 (25.4–29 wt%) and Fe2O3 (4.8–15.2 wt%) are the main major oxides. Samples G and YG present the most suitable physico-mechanical properties for fired bricks between 850 and 1100 °C (i.e. water absorption 19–29%, bulk density 1.49–1.81 g/cm3, compressive strength 12–23 MPa, metallic sonority, good cohesion). On the contrary, the samples R and B show poor physico-mechanical properties during firing due to their low fluxing agent (feldspar) content and high Fe2O3 content (9–15 wt%). The neoformation of mullite, spinel and cristoballite at 1100 °C occurs in specimens favoring the densification of the ceramic body.(Kieufack et al., 2023) |
|
AUTEUR: Hamadou, T., Kanouo, N. S., Dikwa, J., Tchamba, A. B., & Duna, L. L. (2023). TITRE: Cement kiln dust in CIMENCAM Figuil (North Cameroon) : Characteristics and recycling as additives for blended cement production. REFERENCE: SN Applied Sciences, 5(7), 181. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-023-05401-z ABSTRACT This work presents the manufacture of CKD-blended cement from raw materials such as clinker, gypsum, marble and cement kiln dust (CKD) obtained from CIMENCAM Figuil, North Region of Cameroon. The raw materials were first characterized through XRF chemical analyses. Chemical tests (proportion of free lime, loss on ignition, sulfate, and insoluble residues), physical tests (fineness, consistency, setting time, and expansion), and compressive strength tests were carried out on manufactured CKD-blended cements and mortars. Clinker is composed of CaO (65.30%) and SiO2 (21.13%), with significant MgO (2.71%), Na2O + K2O (1.29%), SO3 (0.81%) and lime saturation factor of (97.9); which make this clinker good for cement production. Gypsum is composed of SO3 (36.32%) and CaO (33.92%) but contains very low proportion of impurities; it is therefore classified as low-impurities gypsum suitable for cement productions. The marble is dominantly composed of CaO (37.09%) with significant SiO2 (7.26%), SO3(2.40%), (2.36%), Fe2O3 (1.82%) and MgO (0.18%); it is classified as low-CaO calcitic-aluminosilicate and ferrosilicate bearing marble. The CKD is dominantly made up of CaO (46.0%) and SiO2 (11.62%) with significantly low Na2O + K2O (1.02%), and SO3(2.16%); this classifies it as low alkalies-sulfate cement kiln dust. The proportion of free lime, SO3, loss on ignition, and insoluble residues in the manufactured CKD-blended cements increase with an increase in the proportion of CKD. The blaine specific surface area (BSSA) (4797–6346 cm2/g) and the sieved residues (26.14–30.36%) show an increase with the proportion of used CKD. The compressive strength tests carried out on the prepared brick-shape hardened CKD-cement mortars (at 2, 7, and 28 days) show that, the resistance depends on the proportion of the used CKD (0% control, 5%, 10%, 15%, 20%… up to 50%). Pressures of 17.5 to 11.6 MPa was obtained in 2 days, 28.9 to 20.0 MPa in 7 days, and 35.5–23.3 MPa in 28 days.(Hamadou et al., 2023) |
|
AUTEUR: Tchamba, A. B., Esunsen, J. P., Kanouo, N. S., Duna, L. L., Dikwa, J., Mbessa, M., Gnamsi, G. M. T., Mimpouo, B., Bwemba, C., & Nkeng, G. E. (2024). TITRE: Use of metakaolins from Eseka and Dibamba‐Cameroon as an optimization additive of CEM I Portland cement mortar. REFERENCE: International Journal of Ceramic Engineering & Science, 6(6), e10239. https://doi.org/10.1002/ces2.10239 ABSTRACT The present study deals with two kaolins from Eseka and Dibamba-Cameroon to determine their potential suitability as additive of CEM I 42.5R and to optimize the properties of cement in the sense to promote low-carbon cement. X-ray diffractometry was used to establish the mineralogical composition of two kaolins. X-ray fluorescence was carried out to determine the chemical composition of kaolins and cement. Fine metakaolin powders obtained at 700°C were used as additive in CEM I 42.5R. Furthermore, consistency, setting time, water absorption, compressive and flexural test, and shrinkage test were evaluated. Scanning electron microscopy analysis was carried out to evaluate the microstructure variation. The substitution of CEM I with metakaolin resulted in a considerable increase in compressive and flexural strength from days 7 to 28 at optimum value. The compressive and flexural strengths at 28 days at optimum value of metakaolin increase to 52% and 44%, respectively, explaining the equilibrium oxides in the cement. The maximum values of strength with 20 wt.% MK1 and 30 wt.% MK2 at 7, 14, and 28 days appear in both cases when the ratio of SiO2/Al2O3 is between 2.8 and 2.9. The silica modulus and alumina modulus of cement–metakaolin improved when metakaolin was added. The properties of cement were optimized with a 52% increase in compressive strength at 28 days.(Tchamba et al., 2024) |
|
AUTEUR: Tankeu, J. S. N., Gnamsi, G. M. T., Tchamba, A. B., Ninla, P. L., Kamseu, E., Guidana, M., Nkeng, G. E., Kausik, D., Mbessa, M., & Njopwouo, D. (2023). TITRE: Alteration Analysis of Refractories Bricks Used in Industrial Horizontal Anodes Baking Furnace. REFERENCE: Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 48(12), 16137‑16150. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-023-08089-w ABSTRACT This study analyses the alteration of refractory bricks after 96 baking cycles of anodes baking furnace. A decrease of compressive strength from 48.45 to 32 MPa, respectively, for unused and used bricks were observed. The bulk density obtained by mercury intrusion porosimeter method decreased from 2.48 to 2.38 g/cm3for unused and used bricks; while the bulk density by archimedes method increased from 2.29 to 2.49 g/cm3. The water absorption by Archimedes method is decreased from 6.65 to 5.05 wt.%. While the total porosity obtained by mercury intrusion porosimeter increased from 15.41 to 17.21 wt.% for unused and used bricks. In the same way the total cumulative pore increased from 62.05 to 72.35 mm3/g. While the average pore radius decreased from 5.65 to 1.06 µm, respectively, for unused and used brick. The anode side of brick is deterioted rapidly than hot side of brick. The instrusion porosimetry method seems to be the best method to characterize bulk density and porosimetry of refractory bricks than Archimedes method. Mullite peak seems to be not change, suggesting that a very compacted brick with high mullite content seems to be the best matrix for bricks in anode baking furnace. Silica corrosion is mostly affected in refractory brick than alumina in anodes baking furnace.(Tankeu et al., 2023) |
|
AUTEUR: Duna, L. L., Kaze, C. R., Fekoua, J. N. N., Nzouebet, W. A. L., Kamseu, E., Djocgoue, P. F., Rossignol, S., & Leonelli, C. (2023). TITRE : Performances of laterite-based geopolymer matrice filters on the bacteriological filtration of contaminated groundwater and microstructure. REFERENCE: Journal of Water Process Engineering, 53, 103699. ABSTRACT In this study Rice husk ash (RHA) obtained from rice husk an agricultural waste product is used to produce the laterite based geopolymer matrices. Five different water sources were analysed and passed through the laterite based geopolymer matrices filters (LBGMF). Bacteriological analysis was used to assess the efficiency of the LBGMF. The filters were obtained by altering laterite with different percentages of RHA as 0, 10, 20, 30, 40.wt%. Samples were cured at 80 °C for 24 and 48 h and measured at 2, 7, and 28 days for various tests while others were cured at ambient temperature and measured at 28 days. The results of XRD, FI-IR, ESEM, and MIP investigations were used to establish the effective stability of the laterite based geopolymer matrice filters for water filtration. Best results were obtained at 28 days of curing for compressive and flexural strength, water absorption, bulk density and apparent porosity. Bacteriological parameters (faecal streptococci, faecal coliforms, Escherichia coli) were measured in a contaminated groundwater samples at the inlet and outlet of the laterite based geopolymer matrices filters with two trials assessment. Results demonstrates that the LBGMF produced, contained both mesopores and macropores and with the mesopores suitable for water filtration. These pores were efficient in reducing coliform bacterial present in a highly polluted ground water.(Duna et al., 2023) |
|
AUTEUR: Nana, A., Singla, R., Alomayri, T., Epey, N., Kassem, N. N., Sakue, E. N., Kaze, R. C., Kamseu, E., Kumar, S., & Leonelli, C. (2023). TITRE: Design and characterization of Cameroonian pegmatite-calcined clay binary mortars via geopolymerization. REFERENCE: Journal of Building Engineering, 76, 107078. ABSTRACT In this work, geopolymer binders obtained from a mixture of Cameroonian pegmatite and type 1/1 calcined clays (metakaolin and metahalloysite) at different proportions (10–30 wt%) were used for the formulation of mortars. The kinetic parameters of the reactivity of the pegmatite mixed with different calcined clays in alkaline medium were evaluated via heat of reaction data measured at isothermal conduction calorimeter (ICC) at 27 °C for the first 24 h. As feedstock precursors, the different products obtained were characterized by means of mechanical flexural and compressive resistances (dry and wet), physical properties, Fourier Transform infrared spectroscopy and Scanning Electron Microscope. The results showed that the compressive strength values vary with the type and percentage of calcined clays. The highest values were achieved with mortars containing 30 wt% of the different calcined clays, ranging from approximate 25–35 MPa in dry conditions. The flexural strength values of the mortars increase also with the incorporation of calcined clay and vary from 1.0 to 4.5 MPa. After 72 h of immersion of these samples in water, they lost less than 60% of their mechanical performance. The water absorption rate of the mortars decreases with the incorporation of calcined clays and ranges from 7.5 to 13.8%. FT-IR indicated the reactivity of pegmatite during the geopolymerization process while SEM micrographs exhibited a better cohesion between the aggregates (river sand, 200 μm ≤ ɸ ≤ 2000 μm) and the binder. The above-mentioned pegmatite-calcined clay mortars appear to be a suitable candidate for engineering applications (civil engineering).(Nana et al., 2023) |
|
AUTEUR: S., & Leonelli, C. (2024). TITRE: Effect of milled pegmatite quarry wastes powders on structure, microstructure and mechanical properties of pegmatite-based geopolymers. REFERENCE: Materialia, 33, 102022. ABSTRACT In this investigation, mechanical activation (MA) of pegmatite quarry wastes was perform via an eccentric vibratory mill to improve the geopolymeric reactivity. The MA at miscellaneous times (0 to 90 min) resulted in different activation degrees of samples with improved the fineness of particle size and specific surface area from 2.974 to 5.311 m2.g− 1. Geopolymer binders were synthesized by partly replacing the pegmatite quarry waste with 12.5 wt% of metakaolin. The activating solution used was a mixture of 10 M NaOH and Na2SiO3 solution with a volume ratio of 1:1. Reaction kinetics, compressive strength, water absorption, chemical (FT-IR, XRD, 27Al and 29Si MAS NMR), and microstructural (SEM/EDS and TEM) analyses were done to characterize the obtained geopolymer binders. The microstructural characterization reveals that undissolved/unreacted particles decreased while the non-bridge particles increased with pegmatite milled. Under SEM/EDS and TEM, fineness of pegmatite particles is highlighted by the formation of more reaction product. As a result, the compressive strength of geopolymer binders improved from 22.3 to 51.6 MPa for 0 to 60 min of milling. From these results, there is feasibility of valorising feldspathic (pegmatite) quarry wastes as alternative aluminosilicate precursors to develop environmentally-friendly geopolymer binders. The resulting binders with high-strength and low water absorption (≤ 8.6%) associated to minimization of CO2-emissions can be used as potential candidate in structural applications.(Nana et al., 2024) |
|
AUTEUR: Ribouem A Bessong, C. D., Ottou Abe, M. T., Zounedou Ntieche, Noudem, P., Olinga Mbala, G. F., & Ndjaka, J. M. B. (2023). TITRE : Influence of lithium doping on optoelectronic, electronic, reactivity descriptors, thermodynamic and nonlinear optical properties of dibenzo[b,def]chrysene : Insight by a DFT study. REFERENCE: Optical and Quantum Electronics, 55(11), 1006. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-023-05294-7 ABSTRACT In this article, we predict the optimized structures, the frequency analysis, and determinate quantum chemical descriptors, optoelectronic and electronic parameters; but also nonlinear optical (NLO), thermodynamic properties and Uv–vis absorption spectra of pristine dibenzo[b,def]chrysene (D0) and four of his derivatives obtained by lithium doping (D1, D2, D3, D4). The functionals DFT CAM-B3LYP and B3LYP with the 6–311 + + G(d,p) basis set was used to perform all the calculations. the results show that the doping has considerably reduced the gap energy from 2.879 eV for the pristine molecule D0 to 2.820, 2.698, 2.213 and 1.701 eV respectively for D1, D2, D3 and D4 with the DFT/B3LYP method, a clear improvement in conductivity and semiconductor properties thanks to lithium doping. These semiconductors properties suggest application of our new materials in conception of OLEDs and display devices. Calculated thermodynamic properties such as Gibbs free energy show that these molecules are thermodynamically stable. Doped molecules are very good optoelectronic materials according to very high electric field E values of 4.938 × 109 V m−1 and 4.723 × 109 V m−1 recorded in molecules D1 and D3. These derivatives of dibenzo[b,def]chrysene are also very good non-linear optical materials because of their first-order hyperpolarizability βmol which is greater in all the four cases than that of urea and para-nitro aniline (p-NA) which are references molecules in the non-linear optical domain. Our doped molecules are good candidates for NLO devices conception and realization. Moreover, the doping induces bathochromes effects which leads all our doped derivatives absorb in the visible domain and could be used in the manufacture of organic solar cells.(Ribouem A Bessong et al., 2023) |
|
AUTEUR: Bessong, C. D. R. A., Abe, M. T. O., Ntieche, Z., Noudem, P., Fankam Fankam, J. B., & Ndjaka, J. M. B. (2024). TITRE: Impact of doping with organic dopants and mixed doping with alkali metals and organic dopants on the absorption, electronic, optoelectronic, thermodynamic and nonlinear optical properties of dibenzo[b,def]chrysene in gaseous media : DFT and TD-DFT studies. REFERENCE: Journal of Molecular Modeling, 30(8), 240. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-024-06026-8 ABSTRACT In this study, we evaluate the geometrical, absorption, optoelectronic, electronic, nonlinear optical (NLO) and thermodynamic properties of dibenzo[b,def]chrysene molecule derivatives by means of DFT and TD-DFT simulations. In view of the aim of producing new high-performance materials for non-linear optics (NLO) by doping test, two types of doping were used. We obtained six derivatives by doping with organic dopants (Nitro, amide and ticyanoethenyl) and mixed alkali metal (potassium) and organic dopants. Doping with organic dopants produced molecules A, B and C, respectively when substituting one hydrogen with nitro (NO2), amide (CONH2) and tricyanoethenyl (C5N3) groups, while mixed doping involved considering A, B and C and then substituting two hydrogens with two potassiums to obtain compounds D, E and F respectively. The negative values of the various interaction energies calculated for all the doped molecules show that they are all stable, but also that molecules C and F are the most stable in the case of both dopings. The gap energies calculated at the B3LYP level of theory are all below 3 eV, which means that all the molecules obtained are semiconductors. Better still, compounds C and F, with gap energies of 1.852 eV and 1.204 eV, respectively, corresponding to decreases of 35.67% and 58.18% in gap energy compared with the pristine molecule, are more reactive than the other doped molecules. Mixed doping is therefore a highly effective way of narrowing the energy gap and boosting the semiconducting character and reactivity of organic materials. Optoelectronic properties have also been improved, with refractive index values higher than those of the reference material, glass. This shows that our compounds could be used under very high electric field conditions of the order of 4.164 × 109 V.m−1 for C and 7.410 × 109 V.m−1 for F the highest values at the B3LYP level of theory. The maximum first-order hyperpolarizability values for both types of doping are obtained at the CAM-B3LYP level of theory by C: βmol=92.088× 10−30esu and by F: βmol=129.449× 10−30esu, and second-order values are also given by these same compounds. These values are higher than the reference value, which is urea, making our compounds potential candidates for high-performance NLO applications. In dynamic mode and at a frequency of 1064 nm, at the CAM-B3LYP level of theory, the highest dynamic hyperpolarizability coefficients were obtained by C and F. Hyper-Rayleigh scatteringβHRS, coefficients of the electro-optical Pockel effect (EOPE), EFISHG, third-order NLO-response degree four-wave mixingγDFWM, quadratic nonlinear refractive index n2 were also calculated. The maximum values of n2 are obtained by C (6.13 × 10–20 m2/W) and F (6.60 × 10–20 m2/W), these values are 2.24 times higher than that of fused silica which is the reference for degenerate four-wave mixing so our molecules could also have applications in optoelectronics as wavelength converters, optical pulse modulators and optical switches.(Bessong et al., 2024) |
|
AUTEUR: Mbog, S. M., Bitondo, D., & Duna, L. L. (2023). TITRE: Evaluation of Environmental and Social Impacts of the Extraction Quarry of Raw Materials : Case of the ETOA Clay Quarry, Yaounde 3. REFERENCE: Journal of Geography, Environment and Earth Science International, 27(10), Article 10. https://doi.org/10.9734/jgeesi/2023/v27i10718 ABSTRACT This research work is based on the evaluation of environmental and social impacts of the extraction quarry of raw materials at the Etoa clay quarry in Yaounde III and to propose measures aimed at reducing the different negative impacts. This work was carried out during the period of June 2015 to February 2016 followed by an appropriate methodology to meet the outlined objectives:(1) using the matrix of Leopold and Martin fecteau for the identification and evaluation of impacts, (2) cartography of study zone using ERDAS and QGIS and (3) questionnaire surveys to acquire water consumption demographics were all part of our study. It consisted of under taking site visits to the clay quarry, take pictures, and make household surveys and direct observations, analysis and interpretation of collected data. The results show that, extraction of clay from this area has negative impacts of 76.2% with the most significant on the environment being soil degradation, loss of biodiversity and farmland. Globally, most of the negative impacts are irreversible. The positive impacts are of 23.8% and the most important are, construction of acces road to the clay quarry, protection of the entire clay quarry, creation of job opportunities and increase in economic activities. As a measure to mitigate the negative impacts, shrubs will be planted round the site and exploitation will follow an exploitation plan to create acces in to the quarry. At the end of the extraction of clay this area will be transformed in to fish farming and those whose crops will be touched will be compensated. The different mitigation measures proposed are to reduce or if possible repair all the negative impacts (all the residual negative impacts will all have a minor importance) and this will lead to the acceptance of this project in the area on an environmental point of view and will contribute to the promotion of the sustainable development of Etoa and its environs.(Mbog et al., 2023) |
|
AUTEUR: Arnold, L. L., Raoul, T. T. D., Ghislain, F. C., Duna, L. L., Yannick, T. L., & Luc, N. J. (2024). TITRE: Valorization of Fired Clay Bricks Debris (grog) Using Egg Shell and Coconut Shell in the Synthesis of an Ecological Compressed Earth Blocks : Microstructure and Engineering Properties. REFERENCE: Sustainable Chemical Engineering, 530‑549. https://doi.org/10.37256/sce.5220245166 ABSTRACT The aim of this work is to valorize fired clay brick debris (grog, CH) by using egg and coconut shells in the production of eco-friendly compressed earth bricks for sustainable building materials. Samples were cured at ambient temperature (23 ± 3 °C) and obtained by altering different percentages of (CO) and (CN) at 13%, 26% and 40%, respectively; while another mix design of calcined eggshell and coconut shell were incorporated together into the grog powder. Some comprehensive physico-mechanical properties such as water absorption (WA), bulk density (BD), apparent porosity (AP), moisture content (MC), compressive strength (σ) and elastic modulus (EM) were carried out. Chemical composition, X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis, Fourier Transformed Infra-red (FT-IR), Energy Dispersive X-ray (EDX) analysis and Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) were studied. Results show an increase in compressive strength with increasing percentages of calcined eggshell, from 87CH 13CO, 74CH 26CO, 60CH 40CO as 1.38, 2.70, 3.88 MPa, respectively. For 87CH 13CN, 74CH 26CN, 60CH 40CN coconut shell addition show an increase in the percentages of compressive strength. The bulk density decreases with the increase in percentages of calcined eggshell and coconut shell and the percentage of grog decrease. Linear correlation equtions between mechanical properties and mix proportion were determined. SEM micrograph shows a dense microstructure with an agglomeration on the structure. Results obtained indicates an improvement in the engineering properties due to the addition of eggshell waste and these improved properties are suitable to enhance sustainable eco-friendly building materials. (Arnold et al., 2024) |
|
AUTEUR: Kagonbé, B. P., Nafissa, B., Djeutchou, C., Hamdja, A. N., Djoda, P., Loabé, A. P., Yanné, E., & Venyité, P. (2024). TITRE: Gravel and River sand mining activities in Maroua (Far-North Region, Cameroon) : Environmental and Socioeconomic aspects. REFERENCE: Archives of Agriculture and Environmental Science, 9(1), 126‑133. ABSTRACT Sand and gravel mining are amongst the main factors that induces significant impacts on environment, as a result of growing need for building materials and as a source of income for rural communities. This study was conducted to assess the socio-economic and environmental effects of these activities in Maroua, Cameroon. Its objectives include a description of artisanal mining method and identification of its socio-economic and environmental impacts. The study was conducted in a multidisciplinary approach. During the fieldwork, data were collected using questionnaires and focused group discussions were undertaken with those responsible for managing natural resources in the that area. The results reveal that sand mining activity alter river morphology at a faster rate than normal river process, where river reduction of the extraction areas is significantly larger. These activities were responsible for quick resource depletion and adversely affecting the environment and causing disturbances such as, ecological balance, soil degradation, pollution, infrastructure destruction, as well as conflict between miners and communities. Despite the negative impacts, mining activities generate income for all parties involved in the value chain, including the government. Accordingly, based on the research results, there are concerns about sustainable extraction practices by implementing strict rules and government policies.(Kagonbé et al., 2024) |
|
AUTEUR : Rossignol, S., & Leonelli, C. (2023). TITRE : Natural iron-aluminosilicate as potential solid precursor for supplementary cementitious materials : A comparative study with other aluminosilicates. REFERENCE: Heliyon, 9(7). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e17750 ABSTRACT The objective of this study was to investigate the impact of the geographic and climatic conditions on laterites properties and on geopolymerization based-laterite. Four different laterite deposits in the four geographical zones of Cameroon were studied. This included the center, north, south and west corners of Cameroon, having chemical composition of SiO2 + Al2O3 + Fe2O3 = 88.94, 87.6, 89.13 and 78.97%, respectively. The center and south laterites from the black forest, with high pluviometry and relative humidity, show significant amounts of Fe2O3. While the west laterite from grass field - mountainous areas and the north-laterite from plain arid and semi-arid climate still show lower iron concentrations. The IR absorption bands of the different laterites appear between 1007 and 1047 cm−1; characteristic bands of aluminosilicate. The BET (Brunauer-Emmett-Teller) Specific surface area values are comprised in the range of [21.9, 24.1 m2/g] for non-calcined laterite and between [45.6 and 123.5 m2/g] for laterites calcined at 550 °C and 575 °C. The main particle size values are 5.71, 6.37, 7.43 and 8.45 μm for center-laterite, west-laterite, north laterite and south-laterite, respectively. Although, they differ in the degree of laterization, all the laterites present almost total conversion to geopolymers, due to the presence of amorphous kaolinite and reactive goethite. However, the iron content has significant impact on the globular microstructure. The particle size of laterites, their high values of BET surface area and their significant reactivity make them promising substitutes to metakaolin and other supplementary cementitious materials.(Fekoua et al., 2023) |
|
AUTEUR : Jouin, J., Nouping Fekoua, J. N., Ouamara, L., Piolet, E., Gharzouni, A., & Rossignol, S. (2023). TITRE : Insulating phosphoric acid-based geopolymer foams with water and high temperature resistance. REFERENCE: Construction and Building Materials, 398, 132406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.132406 ABSTRACT This paper aims to determine the feasibility of phosphoric acid-based geopolymer highly porous foams elaborated by a surfactant induced mechanical foaming. The processing and consolidation parameters of the basalt fibers reinforced foams were determined. The influence of the aluminosilicate source on the synthesis of usable samples is reported, showing that the Si/Al ratio as well as the reactivity of the source is crucial to ensure a good consolidation. The effect of the Al/P composition of the geopolymer foam on its properties is also discussed. Two optimal formulations with very good properties (water and temperature resistance, mechanical strength, low thermal conductivity) could be established. Their working properties as well as their main physico-chemical characteristics, allowing to understand their formation mechanism were studied. Both withstood immersion in water and exposition to high temperatures. Their size may also be increased without any difference. Their insulating (61 to 75 mW.m−1K−1) and mechanical performances (80 to 190 kPa) are reported, as well as the study of their networks and microstructures.(Jouin et al., 2023) |
|
AUTEUR: Maraf, M. B., Mountessou, B. Y. G., Merlin, T. F. H., Ariane, P., Fekoua, J. N. N., Yves, T. B. J., Raoul, T. T. D., Zintchem, A. A. A., Bebga, G., Mbouombouo, N. I., & Ramasami, P. (2024). TITRE: Virtual screening, MMGBSA, and molecular dynamics approaches for identification of natural products from South African biodiversity as potential Onchocerca volvulus pi-class glutathione S-transferase inhibitors. REFERENCE: Heliyon, 10(9). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29560 ABSTRACT We investigated 1012 molecules from natural products previously isolated from the South African biodiversity (SANCDB, https://sancdb.rubi.ru.ac.za/), for putative inhibition of Onchocerca volvulus pi-class glutathione S-transferase (Ov-GST2) by virtual screening, MMGBSA, and molecular dynamics approaches. ADMET, docking, and MMGBSA shortlisted 12 selected homoisoflavanones-type hit molecules, among which two namely SANC00569, and SANC00689 displayed high binding affinities of −46.09 and −46.26 kcal mol−1, respectively towards π-class Ov-GST2, respectively. The molecular dynamics results of SANC00569 showed the presence of intermolecular H-bonding, hydrophobic interactions between the ligand and key amino acids of Ov-GST2, throughout the simulation period. This hit molecule had a stable binding pose and occupied the binding pockets throughout the 200 ns simulation. To the best of our knowledge, there is no report of any alleged anti–onchocerciasis activity referring to homoisoflavanones or flavonoids. Nevertheless, homoisoflavanones, which are a subclass of flavonoids, exhibit a plethora of biological activities. All these results led to the conclusion that SANC00569 is the most hypothetical Ov-GST2, which could lead the development of new drugs against Onchocerca volvulus pi-class glutathione S-transferase. Further validation of these findings through in vitro and in vivo studies is required.(Maraf et al., 2024) |
|
AUTEUR: Tsague, F. L., Chimeni, D. Y., Assonfack, H. L., Abo, M. T., Cheumani, A. M. Y., Ndinteh, D. T., & Ndikontar, M. K. (2024). TITRE : Study of oxidation of cellulose by Fenton-type reactions using alkali metal salts as swelling agents. REFERENCE: Cellulose, 31(11), 6643‑6661. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-024-05970-1 ABSTRACT Cellulose from corn straw was oxidized by Fenton-type reagents (FeSO4. 7H2O or CuCl2. 2H2O) using alkaline metal salts (LiCl; NaCl). Cellulose pre-treatment using alkali metal salts (LiCl; NaCl) coupled with a high H2O2 loading (up to 500 kg per ton of pulp) are used as a novel approach to improve the oxidation rate of oxidized celluloses. The oxidation rate was determined by measuring the carboxylic acid and total carbonyl contents of the oxidized cellulose. The oxidized celluloses were characterized by Attenuated Total Reflectance-Fourier Transform Infrared (ATR-FTIR), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and thermogravimetric analyses (TGA). The results show that the oxidation efficiency was improved by using the metal salts and increasing the H2O2 loading for both catalytic systems (Fe2+ or Cu2+). The oxidization rate increased gradually with H2O2 loading up to a maximum 500 kg/t of pulp tested without a considerable loss of cellulose structure. The FTIR results revealed that oxidized celluloses exhibit almost similar predominant hydroxy-based structure as native cellulose with the presence of bands in the regions of 1640–1742 cm−1 characteristic of aldehyde and carboxylic acid groups. The XRD results showed that the crystallinity index slightly decreased from 69.4 to 67–68 and 62–64% after oxidation of the cellulose. The equilibrium moisture contents of oxidized celluloses increased compared to the raw cellulose pulp. The moisture curves fit the page model and exhibits a sub-diffusion process.(Tsague et al., 2024) |
|
AUTEUR: Bachirou, S., Saïdou, Kranrod, C., Nkoulou II, J. E. N., Bongue, D., Abba, H. Y., Hosoda, M., Njock, M. G. K., & Tokonami, S. (2023). TITRE : Mapping in a radon-prone area in Adamawa region, Cameroon, by measurement of radon activity concentration in soil. REFERENCE: Radiation and Environmental Biophysics, 62(4), 427‑439. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00411-023-01042-3 ABSTRACT The radon-prone area of the Adamawa region in Cameroon is characterized by high natural radiation background resulting from the high concentrations of radium-226, thorium-232, and indoor radon. To produce a radon-risk map, radon measurements in soil were carried out in the city of Ngaoundere. The radon activity concentration in soil gas ranged from 256 to 166 kBq m−3 with a mean of 80 kBq m−3 and a standard deviation of 38 kBq m−3. The area is mostly classified as high risk (80%) according to the Swedish classification, and 20% as medium risk. A low-risk area was not observed. Granite-like geology sites were characterized by higher radon concentration. A ratio of about 295:1 was obtained for soil radon gas to indoor radon concentrations, with a positive correlation (R = 0.40), and a transfer factor of 3 per mil. These results demonstrate that in situ measurements of radon concentration in soil can provide accurate information on the level of indoor radon concentrations. Geostatistical and deterministic interpolation techniques have been used to obtain a radon map by comparing the suitability of ordinary kriging and inverse-distance-weighted (IDW) interpolation methods. It turned out that there is not much difference in the prediction errors of the two techniques (Root Mean Square Error = 34.4 for ordinary kriging and 34.3 for IDW). It is concluded that both methods give acceptable results. In situ measurements and geostatistical analysis allow assessment of expected indoor radon exposure in a given area at reduced costs and time required. However, for the investigated area, more research is needed to produce reliable radon-risk maps.(Bachirou et al., 2023) |
|
AUTEUR: Bachirou, S., Saïdou, Mishra, R., Kranrod, C., Hosoda, M., Jalaluddin, S., Sapra, B. K., Kwato Njock, M. G., & Tokonami, S. (2024). TITRE: Thoron exposure in the radon-thoron prone area of the Adamawa Region, Cameroon. REFERENCE: Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 213, 111498. ABSTRACT The radon-prone area of the Adamawa region is characterized by high radon concentrations, where no low-risk area was observed. This study aims to investigate about indoor thoron concentration in this area, using RADUET detectors, thoron progeny monitors and DTPS/DRPS. The indoor thoron concentration ranged between 17 and 1000 Bq m−3, with an average of 131 Bq m−3. 36% of dwellings have thoron concentration less than 100 Bq m−3 while 28% are above 300 Bq m−3. The thoron equilibrium factor of 0.04 was found to be two times higher than the globally assumed value. Thoron progeny contributes on average to 26% (1.9 mSv y−1) of the total inhalation dose. The excess lifetime cancer risk due to thoron progeny is about 5%. These results justify that thoron cannot be neglected when assessing radiation doses. As only radon is regulated, such study will contribute to accelerate the regulation on thoron.(Bachirou et al., 2024) |
|
Activités et résultats du Pôle de recherche en Génie Civil et Architecture (PRGCA) |
|
AUTEUR: Nkotto, L. I. N., Kamgang, G. D., Nkengue, L. P., Kanda, J. S., & Metekong, J. V. S. (2023). TITRE: Characterisation of cementitious composite materials based on calcined clay activated by silicate from rice husk ash and Ingessil silicate-activator : Sodium hydroxide (NaOH). Abstract The ever-increasing cost of cement and its production of harmful carbone dioxide (CO 2) has led development actors to continuously search for less environmentally polluting and low-cost binders. Hence the interest in the valorisation of agricultural resources through the production of different binders such as silicate for the elaboration of geopolymers at low manufacturing temperatures (< 100 C). In this study, Ingessil industrial silicate and rice husk ash silicate were used as pozzolan raw materials to prepare geopolymers with sodium hydroxide as activator at a concentration of 12 M. Two types of samples were developed: geopolymer mortars based on Ingessil silicate and geopolymer concretes based on Ingessil industrial silicate and rice husk ash silicate. Sand and gravel were used as fine and coarse aggregates for the production of geopolymer concretes. They were represented 80% of the mass of the geopolymer concretes according to the standards of elaboration. The porosity values obtained were of the order of 30%, ie water absorption values of about 18%, apparent specific weight of about 5% and bulk density of 1.7%. The mechanical values of BGAC-RHA samples are higher than those of BGAC-I. The physico-chemical properties of geopolymer mortars and concretes were similar.(Nkotto et al., 2023) RFEERENCE: International Journal of Engineering, Science and Technology, 15(2), 23‑35. |
|
AUTEURS : Nkotto, L. I. N., Ntamag, L. J., Nzouakoi, V. C. N., Kanda, S., Ma-A, J. F. M., & Metekong, J. V. S. (s. d.). TITRE: FORMULATION AND CHARACTERISATION OF A TILE BASED ON PLASTIC WASTE AND ALLUVIAL SAND SANAGA-CAMEROON. ABSTRACT Background: Plastic bottles of the PET type are still one of the most common pollutants found in Cameroon's cities, particularly in its two major metropolises. They are most often found in periods of flooding irrigated by rivers and agglomerated in catchment areas and in discharge works. Government policies to collect them are weak and do not mainly promote their reuse in view of current research. Objective: The aim of this study is to valorise the use of Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) plastic waste as a binder in the production of roof tiles. Methods: To this end, the melted plastic waste was mixed at different ratios with a 2 mm sieve fraction of Sanaga alluvial sand. The said sand was initially tested and found to be a clean sand, 88.60% sand equivalent, fine grained with a good gradation within the range recommended by NPF18-560. The plastic/sand ratios formulated were: 90/10, 80/20, 30/70, 40/60, 50/50, 60/40, 70/30, 80/20 and 90/10. Results: These samples were subjected to some analysis and it was found that: all the formulations with more than 20% of plastics have a water absorption rate lower than 2.25%, which is in line with the ISO 62: 2008 standard which defines a limit rate of 6% for roof tiles. Furthermore, the porosity test, for the same formulations, shows a rate lower than 4.37%. As for the mechanical characteristics, a high flexural strength ranging from 2.66 to 5.31 MPa was found for formulations ranging from 10 to 50% plastic. Beyond these formulations, the strengths fall continuously for values below 1 MPa. For compressive strength, the following three ratios show better characteristics: 30/70, 20/80 and 90/10 with values of 7.31 MPa, 7.08 MPa and 6.88 MPa respectively. Conclusion: In the end, the ratio with the best characteristics (30/70) made it possible to formulate a Romaine II type tile with optimal impact resistance and waterproofing valued at 540 FCFA per unit. |
|
AUTEURS: Nkotto, L. I. N., Ntamag, L. J., Ma-A, F. J. M., Kanda, J. S., & Metekong, J. V. S. (2023). TITRE: Evaluation of Performances of Calcined Laterite and Oyster Shell Powder Based Blended Geopolymer Binders. Abstract This work consisted in characterizing of calcined laterite and oyster shell powder based blended geopolymer binders. To do this, raw laterite taken from Soa in the city of Yaoundé and oyster shells extracted from Mouanko in the Sanaga-Maritime were initially air-dried, then dried at 105 C, before being calcined at 500 C and 200 C respectively for 2 hours. These samples were subjected to preliminary studies, ie determination of their chemical and mineralogical compositions, particle size distributions, densities, as well as thermal analysis for the synthesis of geopolymer binders. X-ray diffractometry, thermal and gravimetric analysis were carried out on the oyster shell powder and laterite, in order to elucidate the time and degree of calcination of the two samples, the evolution of the linear shrinkage, the setting time as well as the compressive and flexural strengths of the geopolymer binders. The results obtained show that oyster shells are rich in CaCO 3 and contain crystalline phases, while laterite is rich in silica, iron (FeCO 3) and alumina (Al 2 O 3). The geopolymer samples: Lat+ 0% oyster shells have a setting time between 125 and 168 min for a compressive strength of about 47 MPa. The peak strength is observed around 15% addition of oyster shell powder, ie 53.5 MPa at 28 days with an increased setting time. This strength was decreased from 25% of addition of oyster shells, despite the increase observed in the setting time. It appears from this study that the addition of 15% oyster shell increases the compressive strength of the geopolymer, but also leads to a considerable decrease in absorption rate. Above this rate, the compressive strength decreases drastically and concomitantly the setting time increases.(Nkotto, Ntamag, et al. 2023) REFERENCE: Journal of Civil Engineering and Construction, 12(2), 86‑99. |
|
AUTEUR: Kaze, C. R., à Moungam, L. M. B., Metekong, J. V. S., Alomayri, T. S., Naghizadeh, A., & Tchadjie, L. (2023). TITRE: Thermal behaviour, microstructural changes and mechanical properties of alkali-activated volcanic scoria-fired waste clay brick blends. Abstract The present work aims at producing volcanic scoria (Zg) based geopolymer containing high volume of waste fired clay brick (WB). The objective was producing Zg-based geopolymer incorporating WB powders up to 50 wt% and then investigated a potential thermal stability. All formulated samples were prepared with sodium silicate made from rice husk ash and 6 M of an aqueous NaOH solution. The first series of consolidated geopolymer samples were cured at 25 °C, while the second ones were exposed to high temperatures of 400, 600 and 800 °C. The specimens were subjected to mechanical performance, physicochemical and microstructural properties evaluation. The results indicated that incorporating the WB positively influenced the physicochemical performances of geopolymers. Sample prepared with 10 wt% of WB gave highest mechanical property (33 MPa) at 600 °C. The use of WB favoured the densification and strength development of end products in the range of 25–600 °C.(Kaze et al. 2023) REFERENCE: Developments in the Built Environment, 14, 100153. |
|
AUTEUR : Nkotto, Ludovic Ivan Ntom, Blanche Marcelline Manjia, Ekode Rodin Wilson, Jordan Valdès Sontia Metekong, et Sontia Metekong. 2023. TITRE: « Optimisation of the choice of the sizing method for drinking water networks in the developing countries: A case of Cameroon ». Abstract In developing countries (DC), particularly in Cameroon, the demand for drinking water is increasing. To date, the methods of design, sizing and extension of existing drinking water networks are done through the EPANET application which is a simulation software based on the Hardy-Cross method. The main objective of this study is to set up a local tool adapted to the context of DC allowing the design, sizing and extension of networks based on the rough model method (RMM). Thus, on the basis of a previously modelled existing network, a comparison was made between the Hardy-Cross method and the RMM (according to the criteria: costs, speed of execution, aptitude for automation, fidelity and precision) with the multi-criteria analysis tool PROMETHEE II. The results of this analysis show that the best adapted method for the design, sizing and extension of drinking water networks is the RMM. It appears that the setting up of water supply networks in DC must be done by the RMM for affordable costs, rapid execution, easy reproducibility and reliable precision.(Nkotto, Manjia, et al. 2023) REFERENCE : International Journal of Engineering, Science and Technology 15 (1): 13‑25. |
|
Activités et résultats du Pôle de recherche en Génie Mécanique et Métallurgique (PRGMM) |
|
AUTEUR : Joseph, Pondi, Tchotang Theodore, Ntamack Guy Edgar, et Nfor Clins Wiryikfu. 2024. TITRE: « Effect of Short Banana Fibers on the Physico-Mechanical Properties of Cementitious Matrix Mortars at Young Age ». Abstract The aim of this study was to examine the possible influence of banana trunk fibers on the physical and mechanical properties of a cementitious matrix mortar. The results clearly show that the presence of pseudo-banana trunk fibers in the mortar significantly reduces the mechanical strength due to their low mechanical strength and the method of treatment before incorporation into the mortar. And as might be expected regarding physical properties, the higher the fiber content, the more water the mortar absorbs and the more porous and therefore lighter it is. To improve the mechanical properties of the mortars, it was necessary to repeat other formulations by treating the fibers with 6% sodium hydroxide. As a result, new mortar formulations were developed with the same proportions of fiber, and their studies showed an improvement in the mechanical properties in flexion and compression.(Joseph et al. 2024) REFERENCE: International Journal of Pavement Research and Technology, janvier. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42947-023-00410-y. |
|
AUTEURS : Ze, Éric Parfait, Jean Calvin Bidoung, Wolfgang Nzié, Théodore Tchotang, et Bienvenu Kenmeugne. 2024. TITRE: « Influence of the Extraction Method on the Chemical, Physical and Mechanical Characteristics of Oil Palm (Elaeis Guineensis) Petiole Fibers for the Reinforcement of Composite Materials ». Abstract For their use in polymer and composite materials engineering, and with a view to sustainable development, a great deal of work has been carried out with the aim of describing the properties of plant fibers. This work presents the effects of the extraction method on the chemical, physical and mechanical properties of oil palm petiole fibers (OPPF). To this end, the FPPH to be analyzed were obtained by water retting and chemical retting with soda (5% solution). Their physico-chemical and mechanical characteristics were then studied and compared. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) analysis confirmed the existence of the main components of lignocellulosic fiber (lignin, cellulose and hemicellulose). Lignin was reduced by 22.74%, hemicellulose by 27.33% and cellulose by 16.87% compared to water retting. XRD revealed a crystallinity index of 58.66% for fibers extracted with a 5% sodium solution and 58.51% for fibers extracted with water retting. Soda retting reduces density by 3%. Tensile tests revealed an average tensile strength of 156.082 MPa for water-rubbed fibers and 205.875 MPa for soda-rubbed fibers, Young’s modulus of 3.432 GPa for water-rubbed fibers and 5.346 GPa for soda-rubbed fibers. Elongation at break for FPPH extracted by water retting was 5.178% and 4.41% respectively. This shows that the extraction method affects mechanical properties (flexibility and stiffness) and should be chosen according to the desired characteristic.(Ze et al. 2024) REFERENCE: Journal of Thermoplastic Composite Materials 37 (8): 2571‑88. https://doi.org/10.1177/08927057231216743. |
|
AUTEUR: Wembe, Brillant Djomsi, Nfor Clins Wiryikfu, Guy Edgar Ntamack, Bienvenue Kenmeugne, Theodore Tchotang, Djomi Rolland, et Tido Tiwa Stanislas. 2023. TITRE: « Extraction and Physicochemical and Thermomechanical Characterizations of Water Hyacinth Fibers Eichhornia Crassipes ». Abstract The presence of floating plants is becoming an uncontrollable issue on the banks of Douala, Cameroon, notably in the city of Bonaberi, where the water hyacinth is expanding incredibly quickly. The aim of this study is to evaluate the mechanical and physicochemical performance of water hyacinth fibers for pulp manufacture. To this end, tensile tests on fiber bundles in accordance with ISO 13934‐1:2013, thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), chemical composition evaluation in accordance with ASTM 1972 and 1977, and absorption rate were carried out. The results obtained indicate that the fiber is composed of a variety of fibrils with irregular cross‐sections, with an average diameter ranging from 0.02 to 0.09 mm. The fibers absorb 42.03% of their weight in water, and their density ranges from 1.23 to 1.45 g/cm3. According to mechanical tests, the fiber has a maximum tensile strength of around 0.64 MPa, a specific modulus of 6.45 MPa/g/cm3, and an elongation at break of 1.8%. For the chemical characteristics of the fiber, cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin contents are 68.3%, 11.3%, and 7.4%, respectively, while pectin and ash content concentrations are 4.8% and 7.8%, respectively. Thus, in order to determine whether the plant is suitable for making pulp and paper, this investigation was conducted to examine its fiber properties. It was found that the water hyacinth fibers were superior to flax straw and jute fibers in all qualities, but not as good as silk cotton and bagasse fibers. Given the information above, water hyacinth has been recognized as a potential raw material for the pulp and paper industries, though.(Wembe et al. 2023) REFERENCE: Édité par Sheraz Ahmad. International Journal of Polymer Science 2023 (octobre):1‑9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2023/6652978. |
|
Résultats du Pôle de recherche en Géologie, Sciences de l’Environnement et Domaines associés (PRGE) |
|
AUTEUR : Kagonbé, Bertin Pagna, Bakary Souleymanou, Viviane Djaoyang Bakaïné, Raphael Essama Boum Belinga, Bertrand Tatoh Aziwo, Alexis Ngoniri Hamdja, et Likiby Boubakar. 2023. TITRE: « Assessment of Soils Developed on Various Formations in Maroua (Far North, Cameroon) for Production of Compressed Earth Bricks ». Abstract One of the most important materials in the building industry is earth brick. The current work focuses on the evaluation of Maroua soils and their potential usage in the manufacturing of Compressed earth blocks (CEB). Four sites (Frolina, Goubeou, Mambang, and Djoulgouf) were chosen to conduct this study. One sample was collected at each location. Physico-chemical and mineralogical characteristics were obtained by using particle size, Atterberg limits, X-ray diffraction, and X-ray fluorescence analysis. Results revealed that sand is the most abundant fraction (36.9% - 50.5%) followed by clay (22.1% - 28.4%) and silt (11.3% - 23.8%). They mostly correspond to sandy soils. Liquid and Plastic limits range between 22.6% to 41% and 16.1% to 24.9% respectively and the plasticity index spans from 6.5% to 20.3%. Plasticity is low for Mambang and Djoulgouf and medium for Goubeou and Frolina soils. Mineralogical composition revealed the presence of smectite, kaolinite, and illite as clay minerals, associated with variable amounts of quartz, goethite, and K-feldspars. Geochemical analyses indicate a high silica content (47.1% - 72.8%) followed by alumina (10.9% - 22.8%) and iron (6.4% - 13.2%). The mineralogical, chemical and physical properties of the studied soils revealed that they are suitable for the manufacture of CEB according to the Cameroon Standards of CEB.(Kagonbé et al. 2023) REFERENCE: Open Journal of Applied Sciences 13 (6): 874‑87. |
|
AUTEUR: Yannick, Tchedele Langollo, Bilkissou Alim, Njoya Mfokou Abdou Nasser, Oumar Ali Taïga, Njoya Moussa Jalil, Belinga Essama Boum Raphael, et Mache Jacques Richard. 2023. TITRE: « Comparative Study of Mortars Made with Sands of Different Geological Origin ».
Abstract The present work is a comparative study of sand mortars from various geological origins to highlight their influence on mortar qualities. Five different sands and the cement CEM II/B–P 42.5R were used to produce mortars with similar water/cement ratios (W/C). These are the “Sanaga” sand from the Sanaga River, the “Wouri” sand from the Wouri River, the Nyambaka basalt sand, the Meiganga granite sand, and the Leboudi gneiss sand. The physical, chemical, and mineralogical features of these sands were used to characterize and classify them. They were then used to formulate mortars, which were analyzed and compared. According to the results of the mortar setting time tests, the initial setting time ranges from 195 minutes for Sanaga sand mortar (MS04) to 210 minutes for gneiss sand mortar (MGN03), passing Wouri sand mortar (MW05) with 200 minutes, basalt sand mortar (MB01) with 198 minutes, and granite sand mortar (MGR02) with 196 minutes. The final setting time ranged from 496 minutes (MGR02) to 510 minutes (MGN03), with an average of 300 minutes added to the initial setting time. The flexural strength tests of the mortars reveal that crushed sands outperform alluvial sands. They range from 1.64 to 2.18 MPa after 2 days, 3 to 3.90 MPa after 7 days, and 7 to 14.84 MPa after 28 days. The results of the compressive strength tests show that quarry sand mortars have greater average compressive strengths than alluvial sand mortars, with basalt sand providing the greatest performance. These strengths range from 6.35 to 10.83 MPa after 2 days, 7.55 to 18.96 MPa after 7 days, and 22.81 to 34.58 MPa after 28 days, with the MB01 being the best sand. These findings reveal that the geological origin of sands, which specifies certain of their physicochemical and mineralogical attributes, has an impact on the properties of mortars. This impact is also influenced by granulometry and organic matter concentration.(Yannick, Alim, et al. 2023) REFERENCE: Édité par Zbyšek Pavlík. Advances in Materials Science and Engineering 2023 (novembre):1‑15. https://doi.org/10.1155/2023/5139325. |
|
AUTEUR: Atourakai, Michael Roi Apiniel, Désiré Tsozué, Simon Djakba Basga, Aubin Nzeugang Nzeukou, Bertin Pagna Kagonbé, et Dieudonné Lucien Oyono Bitom. 2023. TITRE: « Soil Organic Carbon Accumulation in Dry Tropical Mountainous Zone of Cameroon ».
Abstract The present work was designed to study a soil sequence in Mount Mandara, in order to identify the influence of altitude, soil characteristics, and land use on the accumulation of soil organic carbon (SOC). The study was conducted in four sites in the Far-North region of Cameroon, including Zamai, Kossohone, Sir, and Rhumsiki. Three pits were dug down to the weathering horizons in three positions (upslope, mid-slope, and footslope) along a representative toposequence in each site. Samples were taken from each pit at regular increment of 25 cm from the soil surface. The total SOC stock (T-SOCS) contents are 128.63 ± 5.25 Mg ha−1 in Arenosols at Zamai (608 m a.s.l.), 158.248 ± 10.52 Mg ha−1 in Leptosols at Kosohone (865 m a.s.l.), 158.99 ± 13.25 Mg ha−1 in Luvisols at Sir (970 m a.s.l.), and 144.79 ± 24.23 Mg ha−1 in Regosols at Rhumsiki (1050 m a.s.l.). The main secondary minerals are smectite, kaolinite, sepiolite, lepidocrocite, hematite, and calcite. Clay minerals and iron oxides are good receptacle for SOC and might constitute a major asset for the accumulation and the sequestration of SOC. Increase in elevation leads to decrease in the annual temperature which affect microbial activity, leading thus to a slow rate of soil organic matter (SOM) decomposition, which thereby affected SOCS. This is confirmed by the significant correlation between altitudinal gradient and T-SOCS (r = 0.70), with altitude contributing to the accumulation of SOC for 49.68%. Texture also plays a central role in carbon sequestration in the studied area, confirmed by the significant and positive correlation between silt fraction and SOM. Under Regosols, there is a decrease in T-SOCS value as a result of a reduction of the quantity of organic matter returned to the soil and more rapid SOM decomposition due to ploughing. This research provides a preliminary assessment for SOC stock at Mount Mandara. It suggests that altitudinal gradient, land use, and soil characteristics should be included in SOCS models and estimations at local and regional scales.(Atourakai et al. 2023) REFERENCE: Arabian Journal of Geosciences 16 (3): 158. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-023-11248-w. |
|
AUTEUR : Moctar, Iyammi Bintou, Tchedele Langollo Yannick, Alarba Sam-Tunsa Albertine, Jacques Richard Mache, et Nchare Mominou. 2023. TITRE: « Physico-Chemical, Mineralogical Characterization, and Ceramic Properties of Clay Materials from South Mindif (Far North, Cameroon) ».
Abstract Characterization studies of clays are generally carried out to identify possible applications of these materials. This paper describes the physico-chemical, mineralogical, and thermal characterization of residual clays from Mindif commune in Cameroon's Far North Region (Doyang, Mendeo, Mobono, Hoppo, Mindif Center, Tchouake, and Gagadje). Ten samples were taken and studied in the laboratory. The methods used in this work were X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray fluorescence (XRF), infrared spectrometry (IR), thermogravimetric analysis (DTA/TG), particle size analysis by sedimentometry, Atterberg limits, and physical and firing properties at 900 °C, 1000 °C, and 1100 °C. It appears that the particle size distribution is dominated by sand (25–74%), clay (10–48%), and silt (6–27%). They mostly correspond to sandy clay soils (blue values: 1.5–5), with low (7–13%) to high (23%) plastic characteristics. Chemical analyses showed high SiO2 (53–75%) and low Al2O3 (6–14%) contents, followed by Fe2O3, CaO, K2O, and MgO. The clay materials are mainly made up of quartz, which is associated with feldspar, illite, smectite, and kaolinite. Between 900 and 1100 °C, the color of the specimens was mainly orange. The characteristics of the bricks are varied: water absorption (6–27%), linear shrinkage (1–10%), and flexural strength (4–17 Mpa). A significant development in the densification of ceramic behavior could be noticed at firing temperatures above 1000 °C. The results presented in this article indicate that these clay materials are suitable for the manufacture of earthenware and ceramic products, with or without addition.(Moctar et al. 2023) REFERENCE: JMST Advances 5 (1): 13‑26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42791-023-00047-9. |
|
AUTEUR: Taypondou, Darman Japhet, Jules Hermann Keyangue Tchouata, Yannick Tchedele Langollo, Albertine Alarba Sam-Tunsa, Michael Bodang Moudoh, et Gilbert François Ngon Ngon. 2024. TITRE: « Lateral Evolution and Modeling of Garoua-Boulaï Soil Properties for Use in Earthen Constructions ». Abstract This paper deals with the geotechnical characterization, modeling, and valorization of Garoua-Boulaï soils according to their position in the morpho-landscape. Seven samples were collected based on morphological units defined in the area to assess the progression of their physicochemical and mineralogical properties. Globally, sand (42.23-56.9%) and clay (26.77-42.27%) are the most common granular classes, while gravel particles (Gr, 0.05-07.8%) and silts (15.5-26.77%) are underrepresented. The plasticity index of the materials investigated ranges from low to medium (10.43-20.21%) from the upper to the lower morphological units. They are rich in silica (SiO2, 37.13-52.83 wt.%), iron oxide (Fe2O3, 4.2-7.8 wt.%), and aluminum (Al2O3, 15.66-17.33 wt.%), while the other oxides are present in smaller amounts (< 10 wt.%). Clay minerals such as kaolinite, chlorite, and illite, in addition to non-clay minerals such as quartz, gibbsite, and hematite, characterize a large proportion of Garoua-Boulaï’s soils. Monosialitization formation process is more pronounced in the upper part, while bisialitization formation process in the lower part prevails for the development of these materials. The materials investigated can be used in earth bricks, pottery, and shallow foundation support. Compressed earth bricks (CEB) had compressive values ranging from 2.2 to 8.63 MPa, with flexural strengths varying from 0.87 to 2.71 MPa. The relationship between physical soil parameters and CEB properties is highlighted by Pearson’s correlation coefficients. The prediction of compressive strength and water absorption from soil physical properties showed good results, with correlation values of 0.96 and 0.71, respectively.(Taypondou et al. 2024) REFERENCE: Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance 33 (22): 12573‑92. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-023-08885-3. |
|
AUTEURS: Yannick, Tchedele Langollo, Liyong Luc Arnold, Taypondou Darman Japhet, Mambou Ngueyep Luc Leroy, Tchamba Arlin Bruno, et Ngounouno Ismaïla. 2023. TITRE: « Properties of eco-friendly cement mortar designed with grounded lead glass used as supplementary cementitious material ». Abstract The purpose of this research is to highlight the effect of adding Leaded Glass Powder (LGP) to cement matrices. To achieve this, glass from Cathode-Ray Tube (CRT) with reactive elements (SiO2 + Al2O3 + Fe2O3) of 26.66% (determined by XRF) is collected and grounded to a particle size of 75 μm, before adding to a CPJ CEM II/A-P 42.5 cement, from 5% to 35% with a step of 5%, to make the pastes and mortars that are subsequently studied during 300 curing days. The analysis results show that the initial setting time increases linearly from 180 min (OPC) to 245 min (35 wt%) and the final setting time from 405 min (OPC) to 550 min (35 wt%). Moreover, LGP additions of 5 wt%, 10 wt%, and 15 wt% show better compressive strengths than OPC after 56 curing days, with 29 MPa, 30 MPa, and 30.9 MPa versus 26.9 MPa for OPC. The corresponding growth rates are 7.8%, 11.52%, and 14.87% respectively. Better compressive strengths are also obtained between 90 and 150 days by adding up to 20 wt% of LGP. At 300 days, only the 10 wt% and 15 wt% substitutions exhibit superior characteristics to OPC (32.1 MPa), with 33 MPa and 34.4 MPa, respectively, which translates to growth rates of 2.8% and 8.41%. The optimal substitution percentage was 15 wt% over the entire cure time investigated. The variations in porosity and water absorption of mortar specimens with the addition of glass show convex trends, indicating good correlations confirmed by the Pearson correlation test results (0.99). Furthermore, these parameters have strong correlations with the curing time (−0.65 and −0.63, respectively) and the compressive strengths (−0.84 and −0.82). The apparent density of the specimens does not describe a uniform variation, as evidenced by the low correlation coefficient with curing time (−0.49), whereas the correlations with porosity (0.76), water absorption (0.76), and compressive strength (−0.6) are strong. According to the hydrate analysis, the Alkali-Silica Reaction (ASR) is marginal in the matrix studied, and the pozzolanic reaction of the second generation involving the free lime of the cement intervenes faster than the pozzolanic reaction of the first generation, which produces the portlandite. The polynomial regression models of compressive and flexural strengths developed have correlation coefficients R2 = 0.94 and R2 = 0.91, respectively. Based on these findings, the substitution rate of cement by CRT glass recommended is 15 wt%.(Yannick, Arnold, et al. 2023) REFERENCE: Heliyon 9 (7). https://www.cell.com/heliyon/fulltext/S2405-8440(23)04744-8. |
|
AUTEURS: Bainamndi, Joseph Daliwa, Emmanuel Siryabe, Guy-Edgar Ntamack, Serge Doka Yamigno, et Pierre Maréchal. 2024. TITLE: « Assessing Acoustic Performance of Building Material: A Finite Element Model for 3D Printed Multilayer Micro-Perforated Panels with Compressed Earth Blocks ». Abstract This study deals with 3D printing multilayered micro-perforated panels (M-MPPs) coupled with buildings materials as compressed earth block for noise reduction applications. The sound absorption coefficient α is utilized as a metric to assess the sound insulation capabilities across a frequency range spanning from 10 to 3000 Hz, then evaluated and validated by numerical and experimental methods. The FEM model developed makes it possible to predict the acoustic absorption of M-MPPs by tuning the frequency range and varying optimized acoustics parameters, considering hole-hole interaction and taking into account visco-thermal effects that are present in compressed earth blocks. It is shown that the shape of perforations and material properties including the porosity rate, arrangement in the design of multilayer micro-perforated structures are identified to play a significant role in the sound performance of the entire structure. In addition, the application of MPP coupled with compressed earth blocks improve the sound absorption capacity of the composite structure. The developed FEM leads to accurate prediction of performance, efficient optimization, and cost effectiveness. Finally, the present study reveals the importance of M-MPPs combined with compressed earth blocks (CEBs) as viable noise reduction materials, particularly relevant for engineering applications and development initiatives in emerging economies.(Bainamndi et al. 2024) REFERENECE: Building Acoustics 31 (3): 247‑67. https://doi.org/10.1177/1351010X241265241 |
|
AUTEUR: Yanze, Gaëlle Annick Nyonda, Linda Lekuna Duna, Rodrigue Cyriaque Kaze, Abdolhossein Naghizadeh, Achille Nana, Kamseu Elie, et Florence Uphie Chinje. 2024. TITRE: « Effects of Chemically Treated Coconut Fibers on the Hydric, Physico-Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Plaster Materials Resulting from Hydrated Clay-Lime Mixtures ». Abstract The present study investigated the use of coconut fibres derived from agricultural waste, treated with a sodium bicarbonate solution, to enhance the properties of thermal insulating plasters made from hydrated clay-lime mixtures. The investigation focused on the effects of treated fibres on the hydric, physico-mechanical, and thermal properties of the plaster. Plasters were prepared using clay stabilized with 4 wt% hydrated lime and varying proportions of treated coconut fibres (0, 2, 4, 6, 8, and 10 wt%). Flexural strength, compressive strength, and hydric tests were conducted on the samples. The results revealed that the inclusion of 4% treated fibres yielded the highest compressive strength of 13.11 MPa. Additionally, the use of coconut fibres treated with a 5 M sodium bicarbonate solution improved the thermal conductivity to 0.31 W/m·K, compared to 0.6 W/m·K for samples without fibres. These findings demonstrate that chemical treatment of fibres significantly enhances both the mechanical and thermal properties of the plaster, suggesting its potential for eco-friendly construction applications.(Yanze et al. 2024) REFERENCE : Innovative Infrastructure Solutions 9 (12): 458. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41062-024-01756-3. |
|
AUTEUR: Tchio, Julson Aymard, Joelle Nadia Nouping Fekoua, Cyriaque Rodrigue Kaze, Juvenal Giogetti Deuton Nemaleu, Juho Yliniemi, Elie Kamseu, Florence Uphie Chinje, et Cristina Leonelli. 2024. TITLE: « Improving Thermal Insulation and Thermal Resistance Properties of Laterite‐based Geopolymer Foams by Direct Foaming ». Abstract This work aims to synthesize new foaming laterite geopolymer foam using laterite, sodium silicate solution, sand, and aluminium powder. The porosity rapidly increased with the addition of the foaming agent. The foam matrix had thermal conductivity values of 0.10 W/m K with 0.7% of Al powder and 0.64 W/m K with 0% of Al powder. For fire resistance, samples exposed to high temperatures (200°C and 500°C) showed increased flexural strength, linear shrinkage at 500°C, and a decrease at 900°C due to structural weakening under high thermal pressure and the appearance of new phases such as nepheline and akermanite in X-ray diffraction analysis. The results also showed that a 30% increase in fine aggregate content increased the strength of the foam matrix, with flexural strength ranging from 5 to 9.1 MPa after 28 days of ambient curing. These laterite geopolymer foams have shown promising thermal insulation and mechanical qualities that are appropriate for building applications.(Tchio et al. 2024) REFERENCE: International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, octobre, e14959. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijac.14959. |
|
AUTEURS : Kieufack, G., Nathalie Fagel, A. B. Tchamba, I. Y. Bomeni, F. Ngapgue, Meriam El Ouahabi, et A. S. L. Wouatong. 2023. TITRE: « Mineralogical and physico-chemical characterization of alluvial clays from Bamendou-Balessing (West Cameroon): Suitability for ceramics ». Abstract The alluvial clays of Bamendou-Balessing (West Cameroon) are characterized to evaluate their potential for ceramic products. Four representative samples collected in the study area were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared (FTIR), differential thermal analysis (DTA) coupled with thermogravimetry analysis (TG), X-ray fluorescence (XRF) and physical analyses (particle size distribution and consistency limits). Firing properties of the specimens making from alluvial clays were determined. The alluvial clays are composed of clay minerals (45–64 wt%) dominated by kaolinite (92–98 wt%) with variable contents of illite (1–7 wt%) and vermiculite (0–2 wt%). The non-clay mineral phases are quartz (19–38 wt%) associated with variable proportions of K-feldspar (1–17 wt%) gibbsite (2–5 wt%) and goethite (1–12 wt%). The thermal behavior of the clayey samples shows dehydration of gibbsite and goethite at 281–288 °C and dehydroxylation of kaolinite at 521–524 °C. SiO2 (34.5–47.4 wt%), Al2O3 (25.4–29 wt%) and Fe2O3 (4.8–15.2 wt%) are the main major oxides. Samples G and YG present the most suitable physico-mechanical properties for fired bricks between 850 and 1100 °C (i.e. water absorption 19–29%, bulk density 1.49–1.81 g/cm3, compressive strength 12–23 MPa, metallic sonority, good cohesion). On the contrary, the samples R and B show poor physico-mechanical properties during firing due to their low fluxing agent (feldspar) content and high Fe2O3 content (9–15 wt%). The neoformation of mullite, spinel and cristoballite at 1100 °C occurs in specimens favoring the densification of the ceramic body.(Kieufack et al. 2023) REFERENCE: Construction and Building Materials 407:133396. |
|
Publications 2020 |
|
Arlin Bruno Tchamba, Michel Mbessa, Tchedele Langollo Yannick, Sandra Waida, Antoine Elimbi, Uphie Chinje Melo & Thomas A. Bier, (2020), Reactivity of calcium disolangealuminate (CaAl4O7) refractory cement with lithium carbonate (Li2CO3) admixture, Journal of Asian Ceramic Societies, 8:2, 223-233, DOI: 10.1080/21870764.2020.1724246. |
|
Boum, R.B.E., Kaze, C.R., Nemaleu, J.G.D. Viviane Bakaine Djaoyang, Nkwaju Yanou Rachel, Patrick Lemougna Ninla, Francois Mvondo Owono, Elie Kamseu (2020), Thermal behaviour of metakaolin–bauxite blends geopolymer: microstructure and mechanical properties. SN Appl. Sci. 2, 1358 https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-020-3138-9. |
|
Djepaze, Yaceinthe & Pagna Kagonbe, Bertin & Madi, Achille & Kamseu, Elie & Ntamack, Guy. (2020), Influence Of The Fineness Modulus Of Sand On The Compressive Strength Of Its Corresponding Mortar: A Mathematical Model Proposal, pages 43, BN: 978-9975-153-76-5 |
|
Eric Parfait, Ze & Tchotang, Theodore & Joseph, Souck & Clins, Nfor & Pondi, Joseph & Arnaud, Mpoung. (2020), Elaboration and Characterization of a Fiber Composite Material Made of Petioles of the Elaeis guineensis (Oil Palm). Open Journal of Composite Materials. 10. 106-117. 10.4236/ojcm.2020.104008. |
|
Cyriaque Rodrigue Kaze, Thamer Alomayri, Assaedi Hasan, Sylvain Tome, Gisèle Laure Lecomte-Nana, Juvenal Giogetti Deutou Nemaleu, Herve Kouamo Tchakoute, Elie Kamseu, Uphie Chinje Melo, Hubert Rahier (2020), Reaction kinetics and rheological behaviour of meta-halloysite based geopolymer cured at room temperature: Effect of thermal activation on physicochemical and microstructural properties, Applied Clay Science, Volume 196, October 10, 5773 |
|
Mbakop, T.T., Deutou, J.G.N., Boubakar, L., Ndigui Billong, U.C. Melo, E. Kamseu, Vincenzo M. Sglavo. (2020), Enhancing the crystallization phenomena and strength of porcelain stoneware: the role of CaO. J Therm Anal Calorim, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09323-5 |
|
Mimboe, Aude & Abo, Marina & Djobo, Jean Noël & Sylvain, Tome & Kaze, Cyriaque & Deutou Nemaleu, Juvenal Giogetti. (2020), Lateritic soil based-compressed earth bricks stabilized with phosphate binder. Journal of Building Engineering. 101465. 10.1016/j.jobe.2020.101465. |
|
Mohamed, Hawa & Deutou Nemaleu, Juvenal Giogetti & Kaze, Cyriaque & Moungam, L.M. & Kamseu, E. & Melo, Uphie & Leonelli, Cristina. (2020), Mechanical and microstructural properties of geopolymer mortars from meta-halloysite: effect of titanium dioxide TiO2 (anatase and rutile) content. SN Applied Sciences. 2. 10.1007/s42452-020-03396-5. |
|
N. Billong, L. Boubakar, B.N. Bayiha; S.M. Njimbouombouo, U.C. Melo, OJ. Kinuthia. (2020), An investigation on the suitability of hydrated building lime from travertine limestone outcrop of Bogongo, South West of Cameroon. Case studies in Construction and Buiding Materials, Elsevier, 13, e00369. |
|
Nouemsi Soubgui, Epiphanie & Theophile, Rufin & Fongang, R.T. & Kamseu, E. & Lissouck, René & Andreola, Fernanda & Boubakar, · & Rossignol, Sylvie & Leonelli, Cristina. (2020), Microstructure and physico‐chemical transformation of some common woods from Cameroon during drying. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry. 10.1007/s10973-020-09890-7. |
|
Pagna Kagonbe, Bertin & Tsozué, Désiré & II, Yaceintthe & Nzeukou, Aubin & Madi, Achille & Basga, Simon & III, Simon. (2020), Physical Characterization and Optimization of Fineness Moduli of Natural Sand from The North Region of Cameroon Used in Construction. Journal of Sustainable Construction Materials and Technologies. 5. 407-419. 10.29187/jscmt.2019.45. |
|
Pagna Kagonbe, Bertin & Tsozué, Désiré & Nzeukou, Aubin & Basga, Simon & Belinga Essama, Raphael & Likiby, B & III, S. (2020), Suitability of lateritic soils from Garoua (North Cameroon) in Compressed Stabilized Earth Blocks production for low-cost housing construction. Journal of Materials and Environmental Science. 11. 658-669. |
|
E Tiffo, JBB Mbah, PDB Belibi, JNY Djobo, A Elimbi( 2020), Physical and mechanical properties of unheated and heated kaolin based-geopolymers with partial replacement of aluminium hydroxide, Materials Chemistry and Physics 239, 122103 |
|
Pondi, Joseph & Joseph, Souck & Mozer, Carlos & Tchotang, Theodore & Wilfried, Nyame, (2020), Improvement of the Thermal Properties of Cement Mortars by Adding Banana Pseudo-Trunkfibres. Open Journal of Civil Engineering. 10. 175-186. 10.4236/ojce.2020.103015. |
|
Soualiou, Njimbouombouo & Dodo, Etone & Yannick, Ondoua & Nangah, Che & André, Njoya & Mouncherou, Oumar & Billong, Ndigui. (2020). Potential of Some Granites from Foumban (West Region of Cameroon) as Fluxing Materials for Ceramics. Journal of Minerals and Materials Characterization and Engineering. 08. 353-363. 10.4236/jmmce.2020.85022. |
|
Tchakouté, H.K., Bewa, C.N., Nadine A. Kesseng, Claus H. Rüscher, Elie Kamseu, Fernanda Andreola, Benoît Nait Ali, Cristina Leonelli. (2020), Production of Porous Poly(phospho-siloxo) Networks for Thermal Insulations Using Low-Value Calcium-Rich Wastes as Pore-Forming Agents. Waste Biomass Valor11, 5857–5875, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-019-00846-z. |
|
Tchamba, A. B., Ntchayi, J. S. T., Deutou, J. G. N., Guidana, M., Likiby, B., & Mbessa, M. (2020). Influence of metakaolin from Mayouom, Cameroon, on the properties of high-grade calcined bauxite sintered at 1500 degrees C, Journal of the Australian Ceramic Society, 56, 1323–1331. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-020-00484-y. |
|
Tchamba, AB, Mbessa, M, Sontia Metekong, JV, et al. Mechanical and microstructural properties of cameroonian bauxite ceramics for ballistic applications. Int J Appl Ceram Technol. 2020; 17: 949– 962. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijac.13383. |
|
Tchedele Langollo Yannick, Mambou Ngueyep Luc Lero Kamga Samen Liliane Vanessa, Tchamba Arlin Bruno, Ngounouno Ismaïla, A.Bier Thomas, (2020), Mechanical and microstructural properties of Cameroonian CPJ NC CEM II/B‑P 42.5R cement substitution by glass powder in the cement paste and mortar, SN Applied Sciences 2(8). |
|
Tchotang, Theodore & Mozer, Carlos & Pondi, Joseph & Njie, Jeme & Clins, Nfor & Eric Parfait, Ze & Joseph, Souck. (2020), Extraction and Characterization of Bagasse Fibres from Sugar Cane (Saccharum officinarum) for Incorporation into a Mortar. Open Journal of Applied Sciences. 10. 521-533. 10.4236/ojapps.2020.108036. |
|
Juvenal Giogetti Nemaleu Deutou, Van Essa L. S. Kamga, Rodrigue Cyriaque Kaze, E. Kamseu, Vincenzo M Sglavo (2020), Thermal behaviour and phases evolution during the sintering of porous inorganic membranes » Journal of the European Ceramic Society, Volume 40, Issue 5, May, Pages 2151-2162. |
|
Ze Eric Parfait, Noah Pierre Marcel, Nnomo Elobi Didine, Nfor Clins Wiryikfu, Betene Ebanda Fabien, Ngahiyi Abbé Claude Valery, Atangana Ateba, (2020), Elaboration and Characterization of Composite Materials Reinforced by Papaya Trunk Fibers (Carica papaya) and Particles of the Hulls of the Kernels of the Winged Fruits (Canarium schweinfurthii) with Polyester Matrix, Journal of Minerals and Materials Characterization and Engineering, Vol.8 No.5 Paper ID 101973, 12 pages, DOI:10.4236/jmmce.2020.85021. |
|
Publications 2019 |
|
Achile Nana, Jean Ngouné, Rodrigue C. Kaze, Likiby Boubakar, Serge K. Tchounang, Hervé K. Tchakouté, Elie Kamseu, Cristina Leonelli, (2019), Room-temperature alkaline activation of feldspathic solid solutions: Development of high strength geopolymers, Construction and Building Materials, volume 195, Pages 258-268,ISSN0950-0618, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.11.068. |
|
Deutou, J.N.G., Zounedou, N., Kaze, R.C., Hawa Mohamed, Tibi Beda, U. C. Melo, Elie Kamseu, Vincenzo M. Sglavo. (2020), Semi-vitrified porous kyanite mullite ceramics: Young modulus, microstructure and pore size evolution. SN Appl. Sci. 2, 126 https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-019-1902-5. |
|
B.N. Bayiha, N.Billong, E. Yamb, R.C. Kaze, R. Nzengwa. Effect of limestone dosages on some properties of geopolymer from thermally activated halloysite. Construction and Building Materials 217,2019, 28–35. |
|
Bewa, C.N., Tchakouté, H.K., Rüscher, C.H. et al. (2019), Influence of the curing temperature on the properties of poly(phospho-ferro-siloxo) networks from laterite. SN Appl. Sci.1, 916. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-019-0975-5. |
|
CR Kaze, Paul Venyite, Achile Nana, Deutou Nemaleu Juvenal , Herve Kouamo Tchakoute, Hubert Rahier, Elie Kamseu, Uphie Chinje Melo Cristina Leonelli, (2019), Meta-halloysite to improve compactness in iron-rich laterite-based alkali activated materials, Materials Chemistry and Physics, MAC 122268 |
|
Dominique E. Tchinda Mabah, Hervé K. Tchakouté, Claus H. Rüscher, Elie Kamseu, Antoine Elimbi, Cristina Leonelli, (2019), Design of low cost semi-crystalline calcium silicate from biomass for the improvement of the mechanical and microstructural properties of metakaolin-based geopolymer cements, Materials Chemistry and Physics, Volume 223, Pages 98-108, ISSN 0254-0584, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2018.10.061. |
|
Flore Mpombo Tchuente, Hervé K. Tchakouté, Charles Banenzoué, Claus H. Rüscher, Elie Kamseu, Fernanda Andreola, Cristina Leonelli, (2019), Microstructural and mechanical properties of (Ca, Na)-poly(sialate-siloxo) from metakaolin as aluminosilicate and calcium silicate from precipitated silica and calcined chicken eggshell, Construction and Building Materials, Volume 201, Pages 662-675, ISSN 0950-0618, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.12.219. |
|
Hamed I. Riyap, Christelle N. Bewa, Charles Banenzoué, Hervé K. Tchakouté, Claus H. Rüscher, Elie Kamseu, Maria C. Bignozzi & Cristina Leonelli, (2019), Microstructure and mechanical, physical and structural properties of sustainable lightweight metakaolin-based geopolymer cements and mortars employing rice husk, Journal of Asian Ceramic Societies, 7:2, 199-212, DOI: 10.1080/21870764.2019.1606140 |
|
Kamseu, E. & Kaze, Cyriaque & Fekoua, Joëlle Nadia & Melo, Uphie & Rossignol, Sylvie & Leonelli, Cristina. (2019), Ferrisilicates formation during the geopolymerization of Natural Fe-rich aluminosilicate precursors. Materials Chemistry and Physics. 240. 122062. 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2019.122062. |
|
Lemougna, Patrick & Nzeukou, Aubin & Aziwo, B. & Tchamba, Arlin Bruno & Wang, Kaituo & Melo, U.. (2019), Effect of slag on the improvement of setting time and compressive strength of low reactive volcanic ash geopolymers synthetized at room temperature. Materials Chemistry and Physics. 239. 122077. 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2019.122077. |
|
Liuhua, Yang & Wu, Aixiang & Li, Hong & Tchamba, Arlin Bruno & Bier, Thomas. (2019), Shear thinning and thickening of cemented paste backfill. Applied Rheology. 29. 80-93. 10.1515/arh-2019-0008. |
|
Nkwaju, Rahel & Djobo, Jean Noël & Fekoua, Joëlle Nadia & Paul William, Huisken & Deutou Nemaleu, Juvenal Giogetti & Courard, Luc. (2019), Iron-rich laterite-bagasse fibers based geopolymer composite: Mechanical, durability and insulating properties. Applied Clay Science. 183. 10.1016/j.clay.2019.105333. |
|
Tchamba, Arlin Bruno & Mbessa, Michel & Jordan Valdès, Sontia Metekong & Liuhua, Yang & Jeanne Solange, Ntchayi & Nkeng, George & Njopwouo, Daniele & Bier, Thomas. (2019), Mechanical and Microstructural Properties of Cameroonian Bauxite Ceramics for Ballistic Applications. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology. 10.1111/ijac.13383 |
|
Zenabou, Ngouloure & Benoit-Ali, Nait & Zékeng, Serge & Rossignol, Sylvie & Melo, Uphie & Tchamba, Arlin Bruno & Kamseu, E. & Leonelli, Cristina. (2019), Improving insulation in metakaolin based geopolymer: Effects of metabauxite and metatalc. Journal of Building Engineering. 23. 10.1016/j.jobe.2019.01.012 |
|
Publications 2018 |
|
Cyriaque Rodrigue Kaze, Herve Kouamo Tchakoute, Theophile Tchakouteu Mbakop, Jacques Richard Mache, Elie Kamseu, Uphie Chinje Melo, Cristina Leonelli, Hubert Rahier, (2018), Synthesis and properties of inorganic polymers (geopolymers) derived from Cameroon-meta-halloysite Ceramics International. |
|
E. Kamseu, H. Mohamed, J.C. Sofack, Duangrudee Chaysuwan, H. K. Tchakoute, J. N. Y. Djobo, S. Rossignol, C. Leonelli. (2018),Moisture Control Capacity of Geopolymer Composites: Correlation of the bulk composition-Pore network to the Absorption-Desorption behavior. Transport in Porous Media DOI:10.1007/s11242-017-0990-1. |
|
Hervé K Tchakouté Daniel Fotio, Claus H Rüscher, Elie Kamseu, Jean N Y Djobo, Maria C Bignozzi Cristina Leonelli, (2018), The effects of synthesized calcium phosphate compounds on the mechanical and microstructural properties of metakaolin-based geopolymer cements Construction and Building Materials Volume 163, 28 February 2018, Pages 776-792: . |
|
N J G Deutou, T Beda M Biesu, L Boubakar, U C Melo, E Kamseu, V M Sglavo, (2018), Design and characterization of porous mullite based semi-vitrified ceramics Ceramics International Volume 44, Issue 7, May 2018, Pages 7939-7948: . |
|
N. Billong,J. Kinuthia, J. E. Oti, U.C. Melo, Performance of sodium silicate free geopolymers from metakaolin (MK) and Rice Husk Ash (RHA): Effect on tensile strength and microstructure. Construction and Building Materials 2018, 189:307-313. |
|
Patrick N. Lemougna, , Kai-tuo Wang, Qing Tang, A.N. Nzeukou, N. Billong, U. Chinje Melo, Cui Xue-min. (2018), Review on the use of volcanic ashes for engineering applications. Resources, Conservation & Recycling, 137 : 177-190. |
|
Rodrigue Cyriaque Kazea, Lynn Myllyam Beleuk à Moungam, Maria Cannio, Roberto Rosa, Elie Kamseu, Uphie Chinje Melo, CristinaLeonelli, (2018), Microstructure and engineering properties of Fe2O3(FeO)-Al2O3-SiO2 based geopolymer composites Journal of Cleaner Production 199: 849-859. |
|
Blaise Ngwem Bayiha, Emmanuel Yamb, Jordan Valdès Sontia Metekong, N. Billong, R. Nzengwa. (2018), Optimizing the Choice of Limestone Deposits for the Production of Portland Cement in Cameroon. International Journal of Materials Science and Applications; 7(5): 174-185. |
|
S. Kumar, J.N.Y. Djobo, A. Kumar, S. Kumar. (2018), Size fractionation of brown fly ash: utilisation of grey fraction as a pozzolanic material in blended cement. European Journal of Environmental and Civil Engineering, DOI:10.1080/19648189.2018.1427635. |
|
S.S.G Hashemi, H.B Mahmud, J.N.Y. Djobo, C.G.Tan, B.C. Ang, N. Ranjbar. (2018), Microstructural characterization and mechanical properties of bottom ash mortar.Journal of Cleaner Production, 170: 797-804. |
|
Sorelle J K Melele, Hervé K Tchakouté, Charles Banenzoué Elie Kamseu Claus H Rüscher Fernanda Andreola Cristina Leonelli, (2018), Investigation of the relationship between the condensed structure and the chemically bonded water content in the poly(sialate-siloxo) network Applied Clay Science Volume 156, May, Pages 77-86: |
|
R Firdous, D Stephan, JNY Djobo, (2018), Natural pozzolan based geopolymers: a review on mechanical, microstructural and durability characteristics ; Construction and Building Materials 190, 1251-1263 45 2018 |
|
Chayanee Tippayasam, Sarochapat Sutikulsombat, E Kamseu, Roberto Rosa, P Thavorniti, Prinya Chindaprasirt, Cristina Leonelli, Greg Heness Duangrudee Chaysuwan, (2018), In vitro surface reaction in SBF of a non-crystalline aluminosilicate (geopolymer) material Journal of the Australian Ceramic Society. |
|
CR Kaze, JNY Djobo, A Nana, HK Tchakoute, E Kamseu, UC Melo, (2018), Effect of silicate modulus on the setting, mechanical strength and microstructure of iron-rich aluminosilicate (laterite) based-geopolymer cured at room temperature, Ceramics International 44 (17), 21442-21450 26 |
|
2017 |
|
Kamseu, L.M. Beleuk Moungam, M. Cannio, Ndigui Billong, Duangrudee Chaysuwan, U. Chinje Melo, C. Leonelli; Substitution of sodium silicate with rice husk ash - NaOH solution in metakaolin based geopolymer cement concerning reduction in global warming, Journal of Cleaner Production xxx (2017) 1e11. |
|
Hervé K. Tchakouté, Claus H. Ruscher, Elie Kamseu, Fernanda Andreola, Cristina Leonelli ; Influence of the molar concentration of phosphoric acid solution on the properties of metakaolin-phosphate-based geopolymer cements; Applied Clay Science xxx (xxxx) xxx-xxx |
|
Kamseu, N.J.G. Detou, N.A. Nzeukou, U.C. Melo, L.G. Magdalena, V.M. Sglavo, T. Beda, C. Lionelli; The role of kyanite in the crystallization and densification of the high strength mullite matrix compsites; J Therm Anal calorim DOI 10.1007/s10973-017-66255-5. |
|
C. Kaze, L.M. Beleuk à Moungam, M.L. Fonkwe Djouka, A. Nana, E. Kamseu, U.C. Melo, C. Leonelli; The corrosion of kaolinite by iron minerals and the effects on geopolymerization; J Therm Anal Calorim DOI 10.1007/s10973-017-6625-5. |
|
Désiré Tsozué, Aubin Nzeukou Nzeugang, Jacques Richard Mache, Suilabayuy Loweh, Nathalie Flagel ; Mineralogical, physico-chemical and technological characterization of clays from Maroua (Far-North, Cameroon) for use in ceramic bricks production ; Journal of Building Engineering 11 (2017)17-2. |
|
Sajedeh Sadat Ghazizadeh Hashemi1, Hilmi Bin Mahmud, Jean Noel Yankwa Djobo, Chee Ghuan Tan, Bee Chin Ang, Navid Ranjbar; Microstructural characterization and mechanical properties of bottom ash mortar; Journal of Cleaner Production 10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.09.191. |
|
Lynn Myllyam Beleuk à Moungam, Hawa Mohamed, Elie Kamseu, Ndigui Billong, Uphie Chinje Melo; Properties of Geopolymers Made from Fired Clay Bricks Wastes and Rice Husk Ash (RHA)-Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH) Activator; Materials Sciences and Applications, 2017, 8, 537-552. |
|
Patrick Lemougna, Kai-tuo Wang, Qing Tang E. Kamseu, N. Billong, U. Chinje Melo, Xue-min Cui; Effect of slag and calcium carbonate addition on the development of geopolymer from indurated laterite; Applied Clay Science 148 (2017) 109–117. |
|
Hervé K. Tchakoute, Claus H. Russser, Kamseu, Jean N.Y.Djobo, C. Leonelli ; The influence of gibbsite in kaolin and the formation of berlinite on the properties of metakaolin-phosphate-based geopolymer cements; Materials Chemistry and Physics 199(2017) 28e288. |
|
Hervé Kouamo Tchakouté, Claus Henning Russer, Malte Hinsch, Jean Noel Yankwa Djobo, Elie Kamseu, Cristina Leonelli; Utilization of sodium waterglass from sugar cane bagasse ash as a new alternative hardener for producing metakaolin-based geopolymer cement. |
|
Jean Noël Yankwa Djobo; Antoine Elimbi; Hervé Kouamo Tchakouté |
|
Sanjay Kumar; Volcanic ash-based geopolymer cements/concretes: the current state of the art and perspectives; Environ Sci Pollut Res (2017) 24:4433–4446 DOI 10.1007/s11356-016-8230-8 |
|
Désiré Tsozué , Aubin Nzeugang Nzeukou, Primus Tamfuh Azinwi , Genesis and classification of soils developed on gabbro in the high reliefs of Maroua region, North Cameroon, Eurasian journal of soils science2017,6 (2)168 -1677. |
|
2016 |
|
Hicham El Boudour El Idrissi, Lahcen Daoudi, Meriam El Ouahabi, Achille Balo Madi, Frédéric Collin, Nathalie Fagel, Suitability of soils and river deposits from Marrakech for the manufacturing of earthenware ; Applied Clay Science 129 (2016) 108–115. |
|
G. N. Deutou1, Hawa Mohamed, N. A. Nzeukou, E. Kamseu, U. C. Melo, T. Beda, C. Leonelli ; The role of kyanite in the improvement in the crystallization and densification of the high strength mullite matrix, Phase evolution and sintering behaviour, J Therm Anal Calorim, DOI 10. 1007 /s 10973 - 016-5686-1. |
|
Hervé K. Tchakouté, Claus H. Rüscher, Sakeo Kong, Elie Kamseu, Cristina Leonelli, Geopolymer binders from metakaolin using sodium waterglass from waste glass and rice husk ash as alternative activators: A comparative study, Construction and Building Materials 114 (2016) 276–289. |
|
Hervé K. Tchakouté, Claus H. Rüscher, Sakeo Kong, Elie Kamseu & Cristina Leonelli, Comparison of metakaolin-based geopolymer cements from commercial sodium waterglass and sodium waterglass from rice husk ash, Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology, (2016) 78:492-506, DOI 10.1007/s10971-016-3983-6. |
|
Hervé K. Tchakouté, Claus H. Rüscher,Sakeo Kong, Elie Kamseu & Cristina Leonelli, Thermal Behavior of Metakaolin-Based Geopolymer Cements Using Sodium Waterglass from Rice Husk Ash and Waste Glass as Alternative Activators, Waste and Biomass Valorization, DOI 10.1007/s12649-016-9653-7. |
|
Tchounang Kouonang, A.S.L. Wouatong, J.G. Deutou Nemaleu, K.P.B. Yerima, D . Njopwouo, Assessment of Ceramic Properties of Fired Clayey Brick Materials from Bamessing in North-West Cameroon (Central Africa), Interceram 65 (2016) [3]. |
|
Elie Kamseu, Isabella Lancellotti, Vincenzo M. Sglavo, Luca Modolo and Cristina Leonelli, Design of Inorganic Polymer Mortar from Ferricalsialic and Calsialic Slags for Indoor Humidity Control, Materials 2016, 9, 410; doi:10.3390/ma9060410. |
|
Elie Kamseu, ChiaraPonzoni, ChayaneeTippayasam, RosaTaurino, Duangrudee Chaysuwan, Vincenzo Sglavo, Parjaree Thavorniti, Cristina Leonelli; Self-compacting geopolymer concretes : Effects of addition of aluminosilicate-rich fines ; Journal of Building Engineering 5 (2016)211–221. |
|
Chayanee Tippayasam, Pongpob Balyore, Parjaree Thavorniti, Elie Kamseu, Cristina Leonelli, Prinya Chindaprasirt, Duangrudee Chaysuwan ; Potassium alkali concentration and heat treatment affected metakaolin-based geopolymer ; Construction and Building Materials 104 (2016) 293–297. |
|
R. MACHE, P. SIGNING, J. A. MBEY , A. RAZAFITIANAMAHARAVO, D. NJOPWOUO AND N. FAGEL, Mineralogical and physico-chemical characteristics of Cameroonian smectitic clays after treatment with low sulfuric acid ; Clay Minerals, (2016) 0, 1–13. |
|
Patrick N. Lemougna, Kai-tuoWang, QingTang, U. ChinjeMelo, Xue-minCui ; Recent developments on inorganic polymers synthesis and applications ; Ceramics International 42 (2016) 15142–15159. |
|
Zo’o Zame Philémon, Nzeukou Nzeugang Aubin, Uphie Chinje Melo, Mache Jacques Richard, Ndifor Divine Azigui, Nni Jean, Typology of Local Construction Materials from the Adamawa and North-West Regions of Cameroon ; Geomaterials, 2016, 6, 50 - 59 Published Online April 2016. |
|
Kamseu, L.M. Beleuk à Moungam, M. Cannio, Ndigui Billong, Duangrudee Chaysuwan, U.Chinje Melo, C. Leonelli ; Substitution of sodium silicate with rice husk ash-NaOH solution in metakaolin based geopolymer cement concerning reducting in ploal Warming, Journal of Cleaner Production ; XXX (2016) 1-11. |
|
Emmanue Yamb, Blaise Ngwem Bayiha, Ndigui Billong and Serykh Inna Robertovna ; Compatibility of Bidzar limestone and Figuil Clay (Northern Cameroon) for the production of Portland Clinker., International Journal of Materials engineering and Technology @ 2016 Pushpa publishing House, Allahabad, India, vol.15, N.1, 2016, page 63-73. |
|
Hervé K. Tchakouté, Claus H. Russer, Sakeo kong, Elie Kamseu, Cristina Leonelli ; Geopolymer binders from metakaolin using sodium waterglass from waste glass and rice husk ash as alternative activators : A comparative study; Construction and Building Materials 114(2016)276-289. |
|
Martine Youmoue, R. Téné Fongang, J. C Sofack, Elie Kamseu, U. Chinje Melo, Ignas K. Tonle, C. Leonelli, Sylvie Rossignol ; Design of ceramic filters using Clay/Sawdust composites: Effect of pore network on the hydraulic permeability; Ceramics International CERI14411 http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j. ceramint. 2016. 12.10 |
|
2015 |
|
Kamseu, Zénabou N. M. NGouloure, BenoîtNait Ali, S. Zekeng, U.C. Melo, S. Rossignol, C. Leonelli, (2015) Cumulative pore volume, pore size distribution and phases percolation in porous inorganic polymer composites: Relation microstructure and effective thermal conductivity, Energy and Buildings, 88, 45-56. |
|
Zénabou N. M. NGouloure, BenoîtNait-Ali , S. Zekeng , Kamseu, U.C.Melo, D. Smith , C. Leonelli, (2015) Recycled natural wastes in metakaolin based porous geopolymers for insulating applications, Journal of Building Engineering, 3, 58-69. |
|
T. Tene Fongang, J. Pemndje, P.N. Lemougna, U. Chinje Melo, C.P. Nanseu, B. Nait-Ali, E. Kamseu, C. Leonelli, (2015)Cleaner production of the lightweight insulating composites: Microstructure, pore network and thermal conductivity, Energy and Buildings, 107, 113-122. |
|
B. Tchamba, J.C. Sofack, R. Yongue, U.C. Melo, (2015) Formulation of calcium dialuminate (CaO•2Al2O3) refractory cement from local bauxite, Journal of Asian Ceramic Societies, 3, 164–172. |
|
L. Wouatong Armand, Tchounang Kouonang Serge, Hawa Mohamed, Yerima K.P. Bernard, Melo Chinje Uphie and Njopwouo Daniel, (2015) Chemical and Mineralogical Characterization of Clayey Deposits for Traditional Pottery and Brickworks in the North West Region of Cameroon (Central Africa),British Journal of Applied Science & Technology,(9)1, 19-36. |
|
Temga Jean Pierre, Nguetnkam Jean Pierre, Balo Madi Achile, Basga Simon Djakba and BitomDieudonné Lucien, (2015) Morphological, physico chemical, mineralogical and geochemical properties of vertisols used in bricks production in the Logone Valley (Cameroon, Central Africa), International Research Journal of Geology and Mining (IRJGM), (5)2, 20-30. |
|
Emmanuel Tiffo, Antoine Elimbi, Joseph Dika Manga and Arlin Bruno Tchamba, (2015) Red ceramics produced from mixtures of kaolinite clay and waste glass, Brazilian Journal of Science and Technology,(2)4,1-13. |
|
Elie Kamseu, Chiara Ponzoni, ChayaneeTippayasam, Rosa Taurino, Duangrudee Chaysuwan, Maria Chiara Bignozzi, Luisa Barbieri, Cristina Leonelli, (2015) Influence of fine aggregates on the microstructure, porosity and chemico-mechanical stability of inorganic polymer concrete, Construction and Building Materials,96 ,473-483. |
|
Chantale N. Djangang, Cristina Tealdi , Alice S. Cattaneo , Piercarlo Mustarelli, Elie Kamseu, Cristina Leonelli, (2015) Cold-setting refractory composites from cordierite and mullite-cordierite design with geopolymer paste as binder: Thermal behavior and phase evolution, Materials Chemistry and Physics,154, 66-77. |
|
Paul-Désiré Ndjigui, Sandrine Appolonie Ebah Abeng, Emile Ekomane, Aubin Nzeugang Nzeukou, Francine Sidonie Ngo Mandeng, Marthe Matoy Lindjeck, (2015) Mineralogy and geochemistry of pseudogley soils and recent alluvial clastic sediments in the Ngog-Lituba region, Southern Cameroon: An implication to their genesis,Journal of African Earth Sciences, 108, 1-14. |
|
R. Mache, P. Signing, J. A. Mbey, A. Razafitianamaharavo, D. Njopwouo and N. Fagel (2015). Mineralogical and physico-chemical characteristics of smectite clays from Cameroon after treatment with weak acid concentrations. Accepted to publish in Clay Minerals (CM2014_03_1_Mache). |
|
Njoya, A. Nzeukou, J.R. Mache, D. Wetshondo, E.pirard, U.C.Melo, et N.Fagel (2015). Valorisation des géoressources pour matériaux locaux de construction en zone périurbaine des pays en voie de développement. Les presses agronomiques de Gembloux. 72-79. |
|
NkalihMefire A., Njoya. A, Yongue Fouateu R., Mache J. R., Nzeukou Nzeugang. , Siniapkine S., Flament P., Melo Chinge U., Ngono A. and Fagel N. (2015). Kaolin occurrence in Koutaba (West-Cameroon): Mineralogical and Physicochemical Characterization for Ceramic Products. Acceptable for publication in Clay Minerals (Ms-EF-15-24). |
|
Elie Kamseu, Chantale Djangang, Paolo Veronesi, Andreola Fernanda, Uphie Chinje Melo, Vincenzo Mario Sglavo, Cristina Leonelli (2015). Transformation of the geopolymer gels to crystalline bonds in cold-setting refractory concretes: Pore evolution, mechanical strength and microstructure. Materials & Design. |
|
Chantale Njiomou Djangang, Elie Kamseu, Claudia Charlotte Tchamo Leussa, Doretta Capsoni, Antoine Elimbi, Daniel Njopwouo (2015). Sustainable Binder From High Amount Of Gibbsite Associated With Kaolinitic. Clay Annales de Chimie - Science des Matériaux 39: 1-2. 75-92. |
|
Uphie Chinje Melo, Patrick N. Lemougna, Jacques Richard Mache, Aubin Nzeukou (2015) Valorisation des résultats de la recherche et entreprenariat local au Cameroun : cas des matériaux de construction, Actes JERSIC 2015, 1-9. |
|
2014 |
|
Chantale Njiomou Djangang, Arlin Bruno Tchamba, Elie Kamseu, Uphie Chinje Melo, Antoine Elimbi, Anna Maria Ferrari, et al. Reaction sintering and microstructural evolution in metakaolin-metastable alumina composites. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry. ISSN 1388-6150. Vol. 117-Number 1 (2014) 1007/s10973-014-3937-6. |
|
Patrick N Lemougna, A Balo Madi, E Kamseu, U Chinje Melo, Mari-Paule Delplancke, Hubert Rahier, Influence of the processing temperature on the compressive strength of Na activated lateritic soil for building applications, Construction and Building Materials,65, 2014, pp 60–66. |
|
N. Lemougna, U.F. Chinje Melo, M.P. Delplancke, H. Rahier, Influence of the chemical and mineralogical composition on the reactivity of volcanic ashes during geopolymers synthesis, Ceramics International, vol.40, Issue 1 part A, p811-820 (2014). |
|
B. Tchamba, U.C.Melo, G.L.Lecomte-Nana, E.Kamseu, C.Gault, R. Yongue, D.Njopwouo. Use of bauxite from Cameroon for solid state sintering and characterization of calcium dialuminate (CaO2Al2O3) refractory cement, Ceramics International 40 (2014) 1961-1970. |
|
2013 |
|
Kamseu, A. Nzeukou, P. Lemougna, N. Billong, U.C. Melo, C. Leonelli, Induration of Laterites in Tropical Areas: Assessment for Potential Structural Applications, Interceram 06/2013 pp 430-437. |
|
Elie Kamseu , Maria Chiara Bignozzi , C. Melo, Cristina Leonelli, Vincenzo M. Sglavo, Design of inorganic polymer cements: Effects of matrix strengthening on microstructure Construction and Building Materials 38 (2013) 1135–1145. |
|
T . Tchakounte Bakop, T. Tene Fongang, U. C. Melo, E. Kamseu, P. Miselli, C. Leonelli (2013) Sintering behaviors of two porcelainized stoneware compositions using pegmatite and nepheline syenite minerals, Journal of thermal analysis and calorimetry. Vol.114, Issue 1, pp113-123 (2013). |
|
Ndigui Billong, Uphie Chinje Melo, Daniel Njopwouo, François Louvet, Jean Pierre Bonnet (2013) Physicochemical characterization of some Cameroonian Pozzolans for use in sustainable cement like materials, Materials Sciences and Applications, , 4, 14-21. |
|
Kamseu, T. Bakop, C. Djangang, U.C. Melo, M. Hanuskova, C. Leonelli, Porcelain stoneware with pegmatite and nepheline syenite solid solutions: Pore size distribution and descriptive microstructure, Journal of the European Ceramic Society 33 (2013) 2775–2784. |
|
Patrick N. Lemougna, F. Chinje Melo, M.P. Delplancke, H. Rahier, Influence of the activating solution’s composition on the stability and thermomechanical properties of volcanic ash-based geopolymers, Construction and Building Materials, 48, 2013, 278–286. |
|
Patrick N. Lemougna, Kenneth J. D. MacKenzie, Guy N. L. Jameson, H. Rahier, F. Chinje Melo, (2013)The role of iron in the formation of inorganic polymers (geopolymers) from volcanic ash: a 57Fe Mössbauer spectroscopy study, J Mater Sci, vol.48, Issue 15, pp 5280 - 5288 (2013). |
|
Nzeukou Nzeugang A., Kamgang Kabeyene V., Medjo Eko R., Melo Chinje U., Njoya A., P. Lemougna, Fagel N., 2013. Industrial potentialities of alluvial clay from Ebebda (Centre Cameroon): influence of lateritic clays admixtures for firing bricks production. Journal of Minerals and Materials Characterization and Engineering, Vol.5, N°1, 236-244. |
|
Nzeukou, N. Fagel, A. Njoya, V. B. Kamgang, R. E. Medjo, U. C. Melo. 2013. Mineralogy and physico-chemical properties of alluvial clays from Sanaga valley (Center, Cameroon): suitability for ceramic application. Applied Clay Science, Vol 83-84, 238-243. |
|
Nzeukou Nzeugang A., Medjo Eko R., Fagel N., Kamgang Kabeyene V., Njoya A., Balo Madi A., Mache J-R., Melo Chinje U. Characterization of clay deposits of Nanga-Eboko (Central Cameroon): Suitability in the production of building materials Clay Minerals, N°48, 655-662. |
|
2012 |
|
B. Tchamba, A.N. Nzeukou, R.F. Tené and U.C. Melo; Building Potentials of stabilized earth blocks in Yaounde and Douala (Cameroon) International Journal of Civil Engineering Research. Volume 3, Number 1 (2012), pp. 1-14 © Research India Publications. |
|
Tsobnang, C. Awono Onana, U. Chinje Melo, Bitjong Ndombol. Formation, Recherche, Innovation et Développement au cœur de l’interdisciplinarité, Actes des 3èmes rencontres EG@, Harmattan, Cameroun, 2012. |
|
2011 |
|
B. Tchamba, E. Kamseu, U.C. Melo, R. Yongue, D. Njopwouo. (2011). Phase and Microstructural Evolution during Densication of Bauxite of Halea-Danielle (Minim-Martap, Cameroun) between 1000 and 1600°C. International journal of Materials Science. ISSN 0973-4589 Volume 6, Number 1, pp. 89-100 © Research India Publications. |
|
Kamseu, C. Leonelli, U.C. Melo, D.S. Perera, P.N. Lemougna. (2011). Polysialate Matrixes from Al-Rich and Si-Rich Metakaolins: Polycondensation and Physico-Chemical Properties. Interceram 60: 01. pp. 25-31. |
|
N. Djangang, E. Kamseu, M.K. Ndikontar, G.L. Lecomte, J. Soro, U.C. Melo, A. Elimbi, P. Blanchart, D. Njopwouo. (2011). Sintering Behaviour of Porous Ceramic Kaolin-Corundum Composites: Phase Evolution and Densification, Materials Science & Engineering A, 528 8311-8318. |
|
N. Lemougna, U.C. Melo, E. Kamseu, A.B. Tchamba. (2011). Laterite Based Stabilized Products for Sustainable Building Applications in Tropical Countries: Review and Prospects for the Case of Cameroon. Sustainability 3: pp. 293-305. |
|
N. Lemougna, J.D. Kenneth MacKenzie, U.C. Melo. (2011). Synthesis and Thermal Properties of Inorganic Polymers (geopolymers) for Structural and Refractory Applications from Volcanic Ash. Ceramics International, 37, pp. 3011-3018. |
|
Obonyo, E. Kamseu, U.C. Melo, C. Leonelli. (2011). Advancing the Use of Secondary Inputs in Geopolymer Binders for Sustainable Cementitious Composites. A Review Sustainability 3: 2, pp. 410-423. |
|
Ndigui Billong, C. Melo, E. Kamseu, J.M. Kinuthia, D. Njopwouo. (2011). Improving Hydraulic Properties of lime–rice Husk Ash (RHA) binders with Metakaolin (MK). Construction and Building Materials 25, pp. 2157–2161. |
|
C. Melo, Ndigui Billong, E.B. Kimaro. (2011). Lime Barium and lime Zinc Glazes with Cameroonian and Tanzanian Raw Materials. Material Science and Applications 2, pp. 1392-1398. |
|
2010 |
|
B. Tchamba, U.C. Melo, E. Kamseu, R. Yongue, D. Njopwouo. (2010). Thermal and Sintering Behavior of Bauxites from Haleo-Danielle, Minim-Martap (Cameroon). Industrial Ceramics 30: 1, pp. 1-6. |
|
2009 |
|
E Kamseu, C Leonelli, D N Perera, U C Melo, P N Lemougna (2009) Investigation of Volcanic ash based geopolymers as Potential Building Materials Interceram 58: 2-3. 136-140 |
|
Leonelli, E. Kamseu, U. C. Melo, A. Corradi, G. C. Pellicani, Descriptive microstructure and fracture surface observations of fired volcanic ash, J Mater Sci (2009) 44:4944–4952. |
|
Ndigui Billong., Melo U.C, Njopwouo D., Louvet F., Bonnet J.P. Effect of mixture constituents on properties of slaked lime-metakaolin-sand mortars containing sodium hydroxide. Cement and Concrete Composite 2009 ; 31: 658 -662. |
|
Ndigui Billong., Melo U.C., Louvet F., Njopwouo D. Properties of compressed lateritic soil stabilized with a burnt clay-lime binder: Effect of mixture components. Construction and Building Materials 2009; 23: 2457-2460. |
|
Kamseu, C. Leonelli, V.M. Sglavo, D.N. Boccaccini, P. Veronesi, U. C. Melo and D. Njopwouo, Alkali-silica Glassy Matrixes (AGM ) as Replacement for Feldspar in Conventional Porcelain Compositions, Sil. Ind. 2009. |
|
2008 |
|
E Kamseu, D N Boccaccini, A Sola, A Rizzuti, C Leonnelli, Melo, U Chinje, N Billong (2008) Sintering behavior, microstructure and mechanical properties of low quartz content vitrified ceramics using volcanic ash pp. 19-26(8) Advances in Applied Ceramics 107:1.19-26. |
|
N. Djangang, A. Elimbi, U.C. Melo, G.L. Lecomte, J. Soro, C. Nkoumbou, J. Yvon, P. Blanchart and D. Njopwouo Sintering of clay-chamotte ceramic composites for refractory bricks. Ceramics International, 34 (2008) 1207-1213. |
|
Cristina Leonelli, Elie Kamseu, U Chinje Melo, Anna Corradi, G Carlos Pellacani (2008) Mullitisation Behavior During Thermal Treatment of three Kaolinitic Clays from Cameroon: Densification, Sintering Kinetic and Microstructure. Interceram 57: 6. 396-401. |
|
B. Tchamba, R.Yongue, U.C.Melo, E.Kamseu, D. Njoya, D. Njopwouo, Caractérisation de la bauxite de Haléo-Danielle en vue de son utilization industrielle dans les matériaux à haute teneur en alumina. Sil. Ind., Vol 73, N° 5-6, pp77 -84, (2008). |
|
Ndigui Billong, Chinje Melo, M.K Ndikontar. Effet du Trona sur les proprités hydrauliques d’un ciment Portland compose. Ndigui Billong, U.Chinje Melo, M.K Ndikontar. Sil.Ind. Volume 73 Nr 1-2, 2008. |
|
N. Djangang, A Elimbi, U.C. Melo, G.L. Lecomte, J.Soro, C, J. Yvon, P. Blancart and D. Njopwouo; Refrectory ceramics from clays of Mayouom and Mvan in Cameroon: Applied Clay science, 39 (2008) 10-18. |
|
2007 |
|
Leonelli, E.Kamseu, D.N. Boccaccini, U.C Melo, A Rissuti, N.Billong and P.Miselli. Volcanic ash as alternative raw materials for traditional vitrified ceramic products. Advances in Applied Ceramics 2007 Vol 106 N°1. |
|
Kamseu Elie, C Leonelli, D N Baccaccini, P Veronesi, P Miselli, Giancarlo Pellacani, U Chinje Melo (2007) Characterisation of porcelain compositions using two china clays from Cameroon Ceramics International 33: 5. 851-857. |
|
N. Djangang, A Elimbi, U. C. Melo, C. Nkoumbou et al, Characteristics and ceramic properties of clays from Mayoum deposit (West Cameroon), Industrial Ceramics, vol 27, N°2, 2007. |
|
2005 |
|
U Chinje Melo, Ndigui Billong, Activité pouzzolanique des déchets de briques et tuiles cuites ; Silicates Industriels, Vol 70 N° 1-2, January-February 2005. |
|
2003 |
|
F. Chinje Melo, E. Kamseu and C. Djangang: Effects of fluxes on the fired properties between 950-1050°C of some Cameroonian clays; Tile § Brick Internat. Volume 19 (2003) [6], 384 – 390. |
|
U Chinje Melo, A. Tcheundem, and N. Nsifa, Fusibility of nepheline Syenite from South Province, Cameroon, Tile § Brick Internat. Volume 19 (2003) [5], 312 – 319. |
|
2001 |
|
Chinje Melo, Production of granite-concrete tiles, African Journal of Building Materials, Vol 05, N°1, 2001. |
|
1990 |
|
F. Chinje and J. H. E. Jeffes: Effects of chemical composition of iron oxides on their rates of reduction. Part 2: Effect of trivalent metal oxides on reduction of hematite to iron. Iron-making and Steel-making, 1990. Vol. 17, N° 5, 317 - 324. |
|
1989 |
|
F. Chinje and J.H.E. Jeffes: Effects of chemical composition of iron oxide on their rates of reduction: Part I – Effect of trivalent metal oxides on reduction of hematite to lower iron oxides. Iron-maling and steel-making, 1989, Vol.16, N°2, 90-95. |
|
1986 |
|
F. Chinje and J. H. E. Jeffes: Evidence of the formation of liquid phase during gaseous reduction of Fe2O3 + Cr2O3 solid solutions at low oxygen potentials and relatively low temperatures. Iron-making and Steel-making, 1986. Vol. 13, N°1, 3 -8. |
|
ANNEE |
PRIX |
BENEFICIAIRES |
TEXTES EXPLICATIFS |
|
2006 |
Prix de l’innovation aux jeunes chercheurs du MINRESI |
NDIGUI BILLONG/ KAMSEU Elie |
Mise au point d’une formulation de micro béton a partir de sable de Monatèle pour la production de tuiles |
|
2007 |
Meilleur chercheur junior lors des Journées d’Excellence de la Recherche Scientifique et de l’Innovation au Cameroun (JERSIC) |
DJANGANG Chantal |
Elaboration des réfractaires aluminosilicates |
|
Meilleur chercheur sénior lors des Journées d’Excellence de la Recherche Scientifique et de l’Innovation au Cameroun (JERSIC) |
Uphie CHINJE MELO |
Valorisation de quelques matériaux à partir des ressources naturelles d’origine minérale et leur vulgarisation |
|
|
2009 |
Meilleur chercheur junior lors des Journées d’Excellence de la Recherche Scientifique et de l’Innovation au Cameroun (JERSIC) |
NDIGUI BILLONG |
Mise au point de 3 formulations du ciment chaux-pouzzolane pouvant substituer le ciment portland pour certaines applications |
|
Meilleur chercheur sénior lors des Journées d’Excellence de la Recherche Scientifique et de l’Innovation au Cameroun (JERSIC) |
Uphie CHINJE MELO |
Valorisation de quelque matériaux a partir des ressources naturelles d’origines minérale pour l’application céramique |
|
|
Prix de l’Excellence du président de la République lors des Journées d’Excellence de la Recherche Scientifique et de l’Innovation au Cameroun (JERSIC) |
Equipe Uphie CHINJE MELO/MIPROMALO |
Valorisation de quelques matériaux a partir des ressources naturelles d’origine minérales pour la croissance de l’emploi |
|
|
2010 |
Meilleur chercheur junior de Third World Academy of Science et Union Africaine (TWAS-UA) |
KAMSEU Elie |
Valorisation des argiles et cendres volcanique dans la production des matériaux céramiques |
|
2011 |
Meilleur chercheur junior lors des Journées d’Excellence de la Recherche Scientifique et de l’Innovation au Cameroun (JERSIC) |
LEMOUGNA NINLA Patrick |
Valorisation de quelques ressources locale pour application dans la construction |
|
2013 |
Meilleur chercheur sénior lors des Journées d’Excellence de la Recherche Scientifique et de l’Innovation au Cameroun (JERSIC) |
Groupe NDINGUI BILLONG/ KAMSEU Elie |
Recherche et développement des matériaux durables pour la construction et l’habitat |
|
2014 |
Meilleur chercheur junior de Third World Academy of Science et Union Africaine (TWAS-UA) |
LEMOUGNA NINLA Patrick |
Valorisation des cendres volcaniques dans la production des matériaux géopolymères |
|
2015 |
Meilleur chercheur junior lors des Journées d’Excellence de la Recherche Scientifique et de l’Innovation au Cameroun (JERSIC) |
LEMOUGNA NINLA Patrick |
Etude et formulation des matériaux géopolymère à base des cendres volcaniques et latérites |
|
Meilleur chercheur sénior lors des Journées d’Excellence de la Recherche Scientifique et de l’Innovation au Cameroun (JERSIC) |
TCHAMBA Arlin Bruno |
Etudes, élaboration et caractérisation des réfractaires et céramiques écologiques: contribution à la valorisation des latérites camerounaises dans les ciments, bétons et briques. |
|
|
2018
|
Meilleur chercheur junior lors des Journées d’Excellence de la Recherche Scientifique et de l’Innovation au Cameroun (JERSIC) |
BEULEUK A. M. Lynn Myryam |
Valorisation des déchets agricoles pour la production des matériaux géopolymères |
|
Meilleur chercheur sénior lors des Journées d’Excellence de la Recherche Scientifique et de l’Innovation au Cameroun (JERSIC) |
Dr KAMSEU Elie |
Production des matériaux céramiques géopolymères et application pour filtration des eaux, routes et logements |
|
|
Meilleur chercheur junior lors des Journées d’Excellence de la Recherche Scientifique et de l’Innovation au Cameroun (JERSIC) |
BEULEUK A. M. Lynn Myryam |
Valorisation des déchets agricoles pour la production des matériaux géopolymères |
|
|
Meilleur chercheur sénior lors des Journées d’Excellence de la Recherche Scientifique et de l’Innovation au Cameroun (JERSIC) |
Dr KAMSEU Elie |
Production des matériaux céramiques géopolymères et application pour filtration des eaux, routes et logements |
|
|
2016-2021 |
Financement de recherche Agence Universitaire de la Francophonie (AUF) |
Dr KAMSEU Elie |
sur fabrication des filtres d’eau : étude de faisabilité à partir des composites argile-bois |
|
2020-2022 |
Financement de recherche « Future Leaders – African Independent Research (FLAIR Fellowships) of the Royal Society (UK) with the African Academies of Sciences (AAS)” |
Dr KAMSEU Elie |
Environmentally-friendly and cold setting process applied to the design of structural and functional matrices for building construction, moisture and water treatment |
AUTRES PRIX
|
N° |
DESIGNATION |
ANNEE |
Observation |
|
01 |
Prix du Président de la République (Lion d’or) lors des Journées d’Excellence de la Recherche Scientifique et l’Innovation au Cameroun (JERSIC) |
2009 |
Prix en équipe : 21 500 000 FCFA |
|
02 |
Third World Academy of Science (TWAS)- African Union (AU), Excellence Young Scientist |
2010 et 2015 |
Prix individuel : 2 000 000 FCFA |
|
04 |
TWAS-UNESCO Grant-N˚ 11 024RG/CHE/AF/AC-G;UNESCO FR: 3240262695. |
|
|
|
05 |
Financement de recherche sur fabrication des filtres d’eau : étude de faisabilité à partir des composites argile-bois |
2016-2020 |
Financement international de la recherche : 40 000 Euros |
|
06 |
Future Leaders – African Independent Research (FLAIR Fellowships) of the Royal Society (UK) with the African Academies of Sciences (AAS) |
2020-2021 |
Financement international de la recherche : 300 000 USD
|
|
N° |
Noms et prénoms |
Grade /Fonction |
Spécialité |
|
DIRECTEUR GENERAL |
|||
|
1 |
Dr LIKIBY BOUBAKAR |
Chercheur, Directeur Général |
Géologie |
|
CHERCHEURS INSTITUTIONNELS |
|||
|
2 |
Dr KAMSEU Elie |
Directeur de recherche |
Chimie inorganique |
|
3 |
Dr NDIGUI BILLONG |
Directeur de recherche |
Chimie inorganique |
|
4 |
Dr TCHAMBA Arlin Bruno |
Maître de recherche |
Chimie inorganique |
|
5 |
Dr LEMOUGNA NINLA |
Chargé de recherche |
Chimie inorganique |
|
6 |
Dr NKWAJU YANOU Rachel |
Chargé de recherche |
Chimie inorganique |
|
7 |
Dr TCHOUNANG KOUANANG Serge |
Chargé de recherche |
Science de la terre |
|
8 |
Dr DEUTOU NEMALEU Juvénal G. |
Chargé de recherche |
Sciences des matériaux |
|
9 |
Dr DJOBO YANKWA Jean Noël |
Attaché de recherche |
Physico-Chimie des matériaux minéraux |
|
10 |
TENE FONGANG Rufin |
Chargé de recherche |
Chimie inorganique |
|
11 |
BALO MADI Achille |
Chargé de recherche |
Chimie inorganique |
|
12 |
BELEUK A MOUNGAM Lynn Myrriam |
Chargé de recherche |
Chimie physique |
|
13 |
HAWA MOHAMED |
Chargé de recherche |
Matériaux et environnement |
|
14 |
CHE RANDY NANGAH |
Chargée de recherche |
Chimie des matériaux |
|
15 |
SOVI Y. Prudence |
Attaché de recherche |
Chimie des matériaux |
|
16 |
SOFACK Jean C |
Attaché de recherche |
Génie civil |
|
17 |
PEMNDJE Joseph |
Attaché de recherche |
Physique appliquée |
|
18 |
TOUKAM TAMNOU Danielle Rosine |
Attaché de recherche |
Management des Organisations |
|
19 |
NGONLEP MIYEMECK Valerie Thérèse |
Attaché de recherche |
Géologie |
|
20 |
BAKAINE DJAOYANG Viviane |
Attaché de recherche |
géologie |
|
21 |
KAGONGE PAGNA Bertin |
Attaché de recherche |
Géologie |
|
22 |
NFOR CLINS WIRYIKFU |
Attaché de recherche |
Génie mécanique |
|
23 |
VENYITE Paul |
Attaché de recherche |
Chimie industrielle |
|
24 |
KAMGA SAMEN Liliane |
Chargée de recherche |
Energétique |
|
25 |
BELINGA ESSAMA BOUM Raphael |
Chargé de recherche |
Géologie |
|
26 |
SONTIA METEKONG |
Attaché de recherche |
Génie civil |
|
27 |
Carlos MOZER |
Chargé de recherche |
Génie mécanique |
|
28 |
SOUCK Joseph Loïc |
Chargé de recherche |
Génie mécanique |
|
29 |
DJEPAZE II Yaceinthe |
Chargé de recherche |
Mécanique et Matériaux |
|
30 |
NTIECHE ZOUNEDOU |
Attaché de recherche |
Science des Matériaux |
|
31 |
GUIDANA Marcel |
Attaché de recherche |
Mécanique et Matériaux |
|
32 |
AZIWO TATOH Bertrand |
Attaché de recherche |
Géologie |
|
33 |
ZE Eric Parfait |
Attaché de recherche |
Technologie de construction industrielle |
|
34 |
NOUEMSI SOUBGUI Epiphanie |
Attaché de recherche |
Génie civil et Architecture |
|
35 |
NTAMAG Jacques Lionel |
Attaché de recherche |
Architecture |
|
36 |
SINA DJAMENI Estelle |
Attaché de recherche |
Génie civil et hydraulique |
|
37 |
OUMAR ALI TAIGA |
Attaché de recherche |
Génie civil |
|
38 |
JEME NJIE TONGA |
Attaché de recherche |
Chimie industrielle et génie de l’environnement |
|
39 |
NOUPING FEKOUA Joëlle Nadia |
Attaché de recherche |
Chimie inorganique |
|
40 |
ONDOUA ABONDO EBENGUE Yannick |
Attaché de recherche |
Sciences environnementales |
|
41 |
ETONE MACKA Alexandre DODO |
Attaché de recherche |
Géosciences des formations superficielles |
|
42 |
NJIMBOUOMBOUO MOULIOM SOUALIOU |
Chargé de recherche |
Géologie minière |
|
43 |
LINDA LEKUNA DUNA |
Attaché de recherche |
Biologie des organismes végétaux |
|
44 |
IBE VERA ITOH |
Attaché de recherche |
Sciences de l’environnement |
|
45 |
PONDI Joseph |
Chargé de recherche |
Génie mécanique |
|
46 |
SOULEYMANOU BAKARY |
Attaché de recherche |
Bactériologie et Virologie médicale |
|
47 |
SOUMAYAH BACHIROU |
Attaché de recherche |
Radiologie et Imagerie médicale |
|
48 |
ADA ZO’O Vanessa Lucie |
Attaché de recherche |
Génie industriel |
|
49 |
ABO Tatiane Marina |
Attaché de recherche |
Génie textile et cuir |
|
50 |
MEY MAHAMAT IMAR |
Attaché de recherche |
Maintenance Industrielle et Productique |
|
51 |
DOUNBISSI KAMGANG Gaëlle |
Attaché de recherche |
Architecture |
|
52 |
NGO KALJOB Thérèse Viviane |
Attaché de recherche |
Ingénieur en bois |
|
53 |
TAM LIKENG Christian |
Attaché de recherche |
Génie civil |
|
54 |
EPEY NOELA ASANJA |
Attaché de recherche |
Sciences environnementales |
|
55 |
LIYONG Luc Arnold |
Attaché de recherche |
Génie industriel |
|
56 |
TCHEDELE LANGOLLO |
Attaché de recherche |
Ingénieur des Mines |
|
57 |
KONTCHIACHOU NKANA Felix Didier |
Attaché de Recherche |
Ingénieur de conception |
|
58 |
BILKISSOU ALIM |
Attaché de recherche |
Génie industriel |
|
59 |
NYAME BOADE Wilfried |
Attaché de recherche |
Génie Industriel |
|
60 |
BODANG Michael MOUDOH |
Attaché de recherche |
Science in Mines and Petroleum |
|
61 |
NTOM NKOTTO IVAN LUDOVIC |
Attaché de recherche |
Génie civil |
|
62 |
ABDOUL BAGUI |
Attaché de recherche |
Génie mécanique |
|
63 |
CHOULAMENKANE BONE Boris |
Attaché de recherche |
Economie et finance |
|
64 |
KEUMEKA JIOFACK Severin Bidias |
Master, Attaché de recherche |
Energie et environnement |
|
65 |
MBA EBODE Robert |
Attaché de recherche |
Génie civil |
|
66 |
MENO TEGUE Vanny Joberthe |
Attaché de recherche |
Architecture |
|
67 |
MAHAMAT ABBA KASSOUM |
Attaché de recherche |
Maintenance Industrielle et productique |
|
68 |
MANJEH MA-A Jane Frances |
Attaché de recherche |
Géotechnique |
|
69 |
KAMDJE NOUENA Ghislain |
Attaché de recherche |
Architecture |
|
70 |
TCHI PEFOUO Wilson |
Attaché de recherche |
Architecture |
|
71 |
ABOMO Thérèse |
Attaché de recherche |
Géotechnique |
|
72 |
MBADI OUM Arles Bienvenu |
Attaché de recherche |
Génie civil |
|
73 |
WILSON RODIN EKODE |
Attaché de recherche |
Construction industrielle |
|
74 |
LOUBE NDOUMBE Marianne Flore |
Attaché de recherche |
Architecture |
|
75 |
ESSOMBA ESSOMBA Constant |
Attaché de recherche |
Géologue |
|
76 |
BELELA AWAM Elodie |
Attaché de recherche |
Géologue |
|
77 |
ETAME KOUETCHEU Kevin |
Attaché de recherche |
Génie Civil |
|
78 |
GARKA SAPOCK Jules Franck Cédric |
Attaché de recherche |
Mine et Pétrole |
|
79 |
MABOU NINKAM Germaine |
Attaché de recherche |
Energie et Environnement |
|
80 |
MOHAMADOU Alpha Ali |
Attaché de recherche |
Génie Sanitaire et Environnement |
|
81 |
MOUSTAPHA |
Attaché de recherche |
Chimie Industrielle et Génie de l’Environnement |
|
82 |
NAFISSA BOUBA |
Attaché de recherche |
Géo-environnement de surface et sub-surface |
|
83 |
NDJONNOU TCHAWA Lynda Phalone |
Attaché de recherche |
Génie Civil |
|
84 |
NFONGOH Thiophine FENJEH |
Attaché de recherche |
Chimie Industrielle et Génie de l’Environnement |
|
85 |
NYAMBI MOHOMYE STEVE Igor |
Attaché de recherche |
Architecture et Construction |
|
CADRES TECHNIQUES ET SCIENTIFIQUES |
|||
|
86 |
ZENABOU NGOULOURE |
Ph.D physique |
|
|
87 |
TCHAKOUNTE MBAKOP T. |
DESS, Chimie Industrielle |
|
|
88 |
DIAMARD Rachel |
Master 2, Génie Civil |
|
INTRODUCTION : Les programmes de Recherche Développement sont axés sur les missions de la MIPROMALO en son article 2 du décret de création N° 90/1353 du 18 septembre 1990; dont le but principal est de valoriser l’emploi des matériaux locaux en vue de réduire les couts de réalisation des équipements nationaux; ils se structurent en trois sous-programmes inscrits dans le programme opérationnel du MINRESI intitulé : DENSIFICATION DE LA RECHERCHE-DEVELOPPEMENT ET DE L’INNOVATION.
Chaque sous-programmes de la MIPROMALO dispose d’une stratégie claire et précise, qui constitue un cadre de référence pour sa mise en œuvre. Le programme support intitulé : GOUVERNANCE ET APPUI INSTITUTIONNEL participe à la facilitation et l’optimisation du fonctionnement de la MIPROMALO.
PROGRAMME OPERATIONNEL DU MINRESI : DENSIFICATION DE LA RECHERCHE-DEVELOPPEMENT ET DE L’INNOVATION
Le but de ce programme est d’appuyer les sciences, la technologie et l'innovation, en offrant des analyses et des conseils et en élaborant des politiques en vue d'améliorer les capacités du Cameroun dans les domaines de Recherche-Développement et d’Innovation. Il couvre l’ensemble des activités des structures opérationnelles de recherche dont les résultats sont mis à la disposition des ministères sectoriels pour exploitation.
OBJECTIF: ACCROITRE LES PERFORMANCES DE LA RECHERCHE SCIENTIFIQUE ET D’INNOVATIONS.
INDICATEUR : NOMBRE DE RESULTATS DE LA RECHERCHE PRODUITS ET DIFFUSES.
Pour la période 2018 - 2020, les activités de recherche, valorisation et de vulgarisation des matériaux locaux à la Mission de Promotion des Matériaux Locaux (MIPROMALO) sont structurées en trois sous-programmes ainsi qu’il suit:
- SOUS-PROGRAMME I : IDENTIFICATION, CARACTERISATION ET TECHNOLOGIES DE TRANSFORMATION DES MATIERES PREMIERES
- SOUS- PROGRAMME II : MISE AU POINT DES TECHNOLOGIES APPROPRIEES DANS LA MISE EN ŒUVRE EFFICIENTE DES MATERIAUX DE CONSTRUCTION
- SOUS-PROGRAMME III : VULGARISATION, FORMATION ET TRANSFERT DES TECHNOLOGIES
PROGRAMME 2 OU SUPPORT DU MINRESI : GOUVERNANCE ET APPUI INSTITUTIONNEL AU SOUS SECTEUR RECHERCHE ET INNOVATION
- SOUS-PROGRAMME IV : GOUVERNANCE ET APPUI INSTITUTIONNEL